38 draw and label an atp molecule
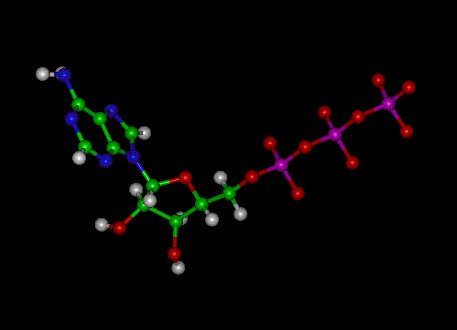
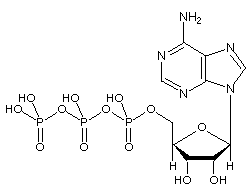
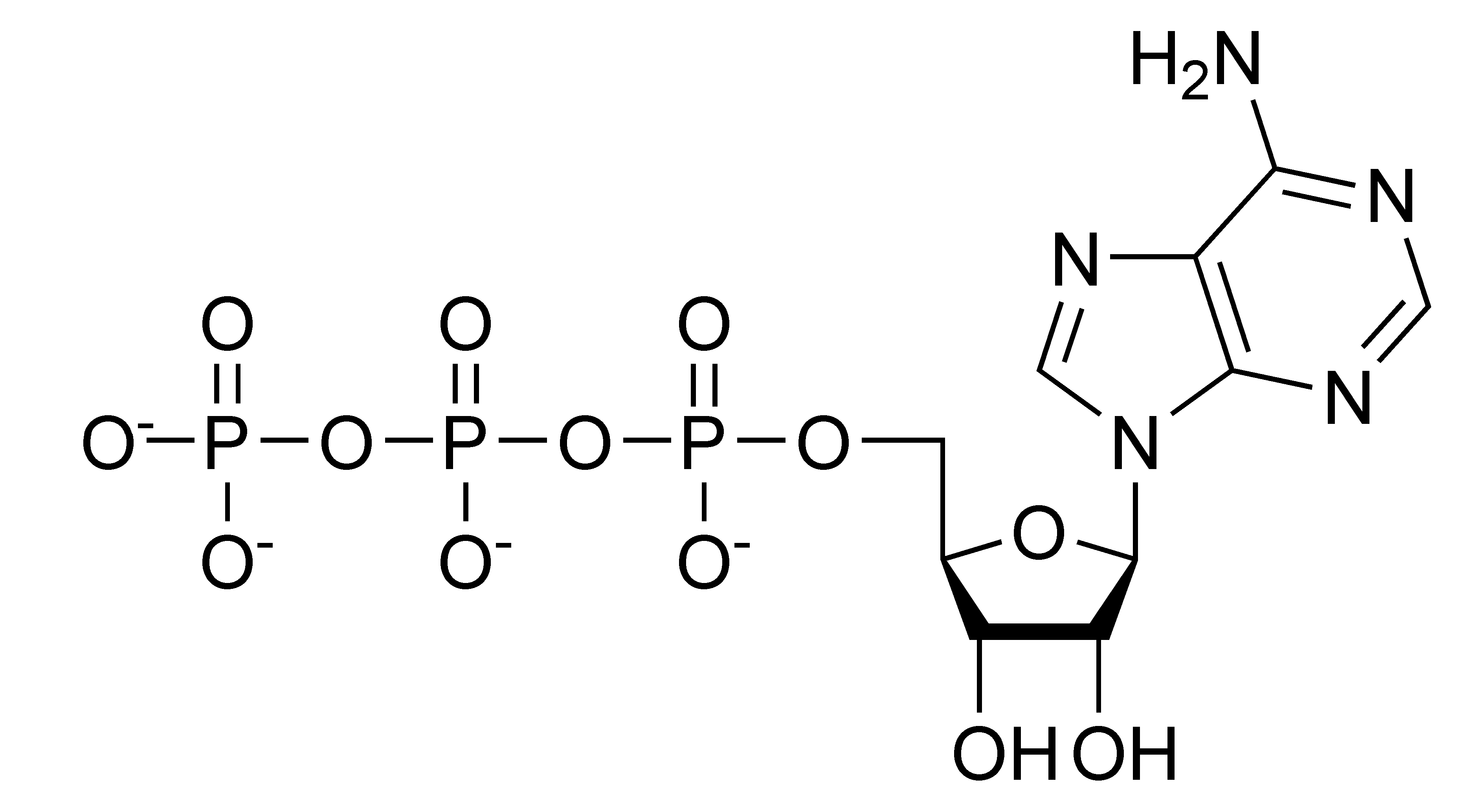
The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. For 3-D Structure of this image using Jsmol Click here CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc.Ribose PAdenine P
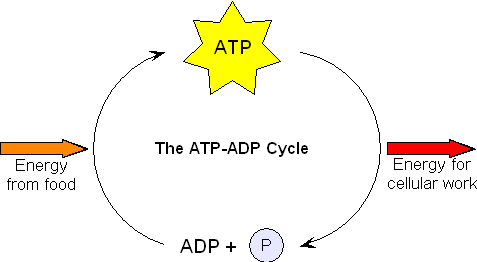
How does atp store and release energy? | Socratic This occurs when a molecule of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) uses the energy released during cellular respiration to bond with a third phosphate group, becoming a molecule of ATP. So the energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups of ATP. When the cell needs energy to do work, ATP loses its 3rd ...
Draw and label an atp molecule
Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Draw and label an ATP model please 1 See answer Advertisement OOp1234 Answer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP. 9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor ATP is a big molecule, but the bond-breaking and bond-forming events we will be studying in this chapter all happen in the phosphate part of the molecule. You will see structural drawings of ATP, ADP, and AMP abbreviated in many different ways in this text and throughout the biochemical literature, depending on what is being illustrated. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
Draw and label an atp molecule. Unit 3 Energy Flow Review Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label the lock-and-key model, including enzyme, substrate, active site, and product. Explain the purpose of a molecule of ATP and where most of the energy is stored in the molecule. ATP molecule basically functions as the power source for the cell. Most of the energy is stored in the bond between the last two phosphates. ATP: Definition, Structure & Function | StudySmarter The definition of ATP in biology ATP or adenosine triphosphate is the energy-carrying molecule essential for all living organisms. It is used to transfer the chemical energy necessary for cellular processes. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy for many processes in living cells. 1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group. Chapters 5b - 7 Honors Biology Flashcards | Quizlet ATP contains energy which can then be used to do other functions in cells such as transport work, mechanical work, and chemical work. The number of ATP's that are produced in: 1. Glycolysis 2. Krebs Cycle 3. Electron Transport Chain 4. Fermentation 5. Total in the 3 phsases of Cellular respiration 1. 2 ATP 2. 2 ATP 3. 28 ATP 4. 0-2 ATP 5. 32 ATP
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6. 5.9: Cellular Respiration - Biology LibreTexts An ATP molecule is like a rechargeable battery: its energy can be used by the cell when it breaks apart into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate, and then the "worn-out battery" ADP can be recharged using new energy to attach a new phosphate and rebuild ATP. ... Draw and explain the structure of ATP (Adenosine Tri-Phosphate). State ... ATP hydrolysis mechanism (video) | Khan Academy That's what I'm going to do in this video. Let's start with our ATP molecule, and let's throw some water in there, H2O. Let's say this is water right here, oxygen with two hydrogens. I'll do the two pairs of oxygen that aren't in bonds right over here, in the outermost shell. Actually let me draw one more water molecule right over here. ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy Structurally, ATP is an RNA nucleotide that bears a chain of three phosphates. At the center of the molecule lies a five-carbon sugar, ribose, which is attached to the nitrogenous base adenine and to the chain of three phosphates. The three phosphate groups, in order of closest to furthest from the ribose sugar, are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma.
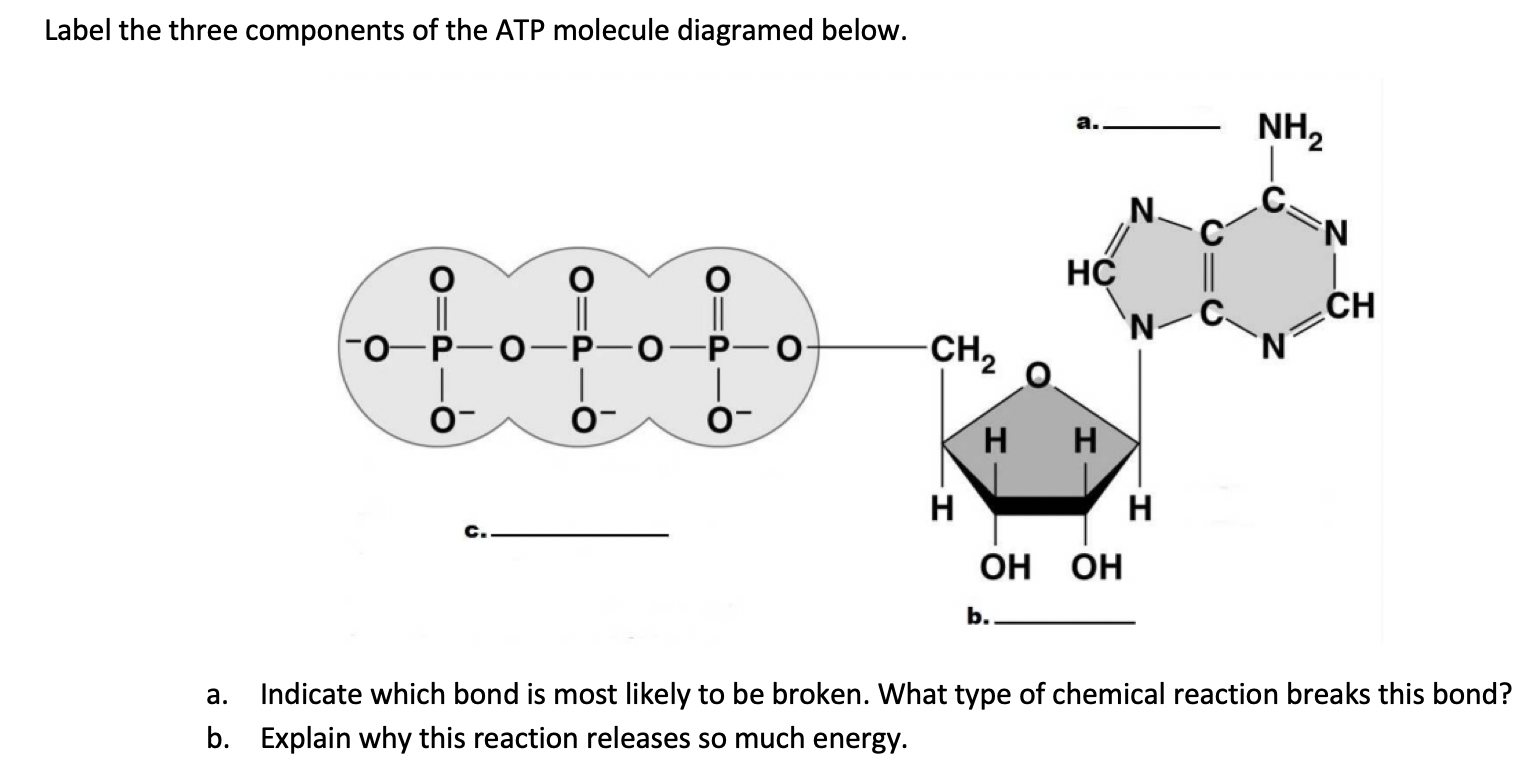
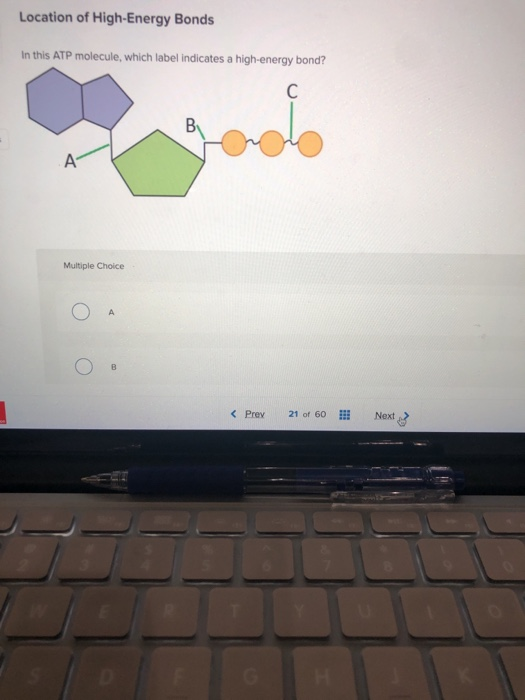
Solved Label each part of the diagram of an ATP molecule | Chegg.com Expert Answer. 100% (1 rating) 7. From left to right- Adenine - Ribose - Phosphate groups 8. The low battery represents an ADP molecule. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP results in loss of phosphate group. hence ADP + Pi is low energy state during ATP (energy carrier) …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label each part of the diagram of ... Adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts small organic molecules including adenosine triphosphate ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures: the nitrogenous base, adenine; the sugar, ribose; and a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. The phosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source which the cell taps. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. 9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor ATP is a big molecule, but the bond-breaking and bond-forming events we will be studying in this chapter all happen in the phosphate part of the molecule. You will see structural drawings of ATP, ADP, and AMP abbreviated in many different ways in this text and throughout the biochemical literature, depending on what is being illustrated.
Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Draw and label an ATP model please 1 See answer Advertisement OOp1234 Answer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
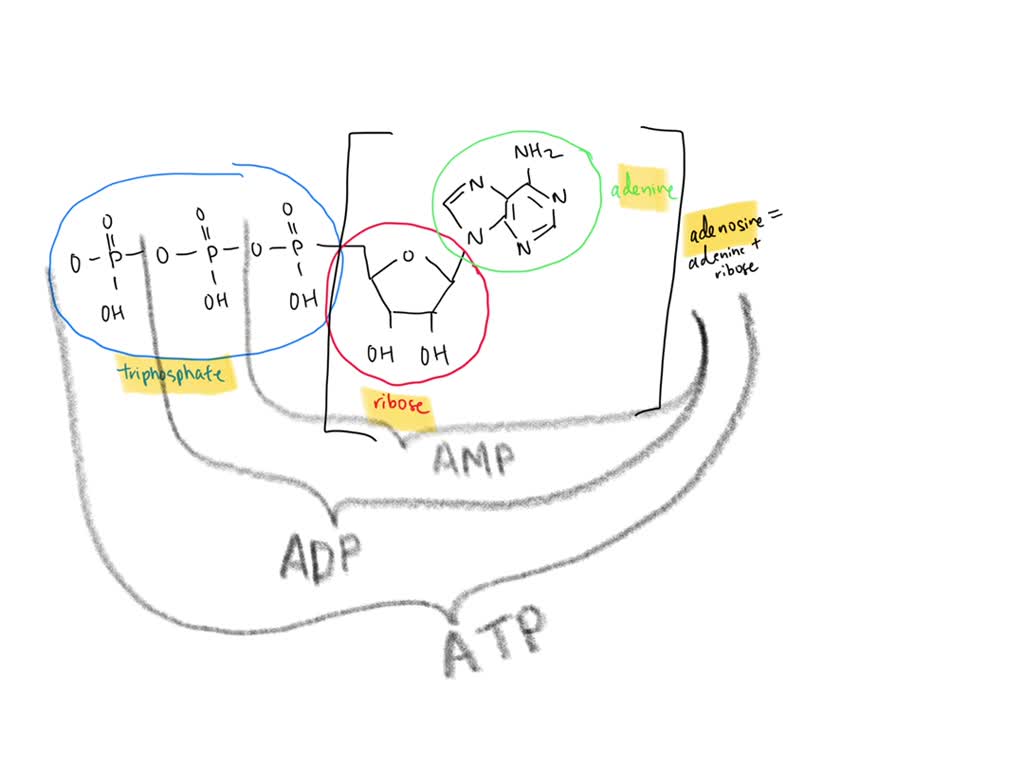
Part B, Draw the chemical structure of ATP, 1. Circle and label the following parts: Adenine, Ribose, Tri-Phosphate., 2. Put a bracket around and label the part that is called Adenosine., 3. Use ...
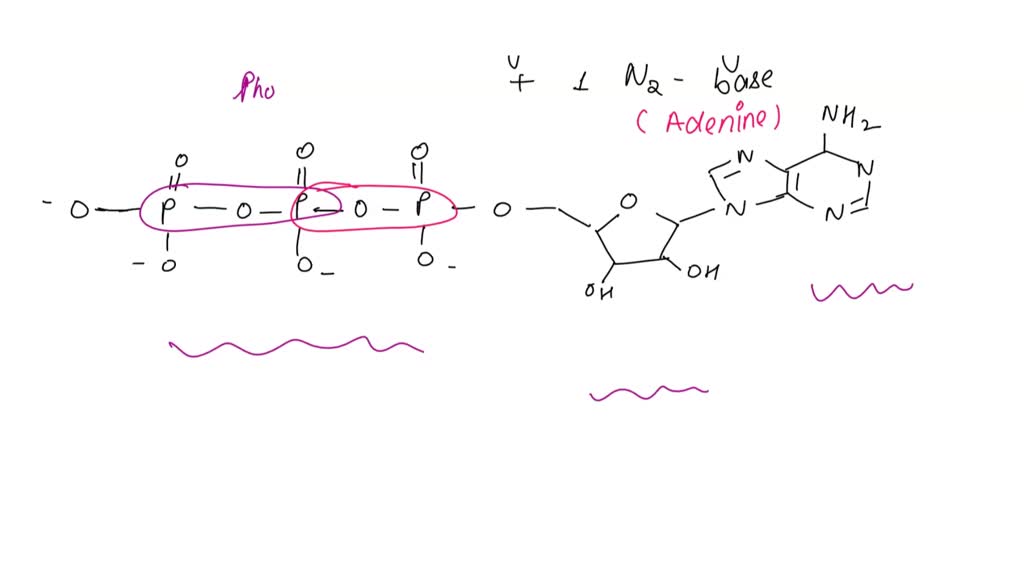
Draw and Iabel an ATP molecule Using molecules release Your energy- drawing, diagram, explain how ATP, How is ADP different from ATP? Adp hc? AaTPAc 7p nc> pkosdhete, TOJp, drps, Explain why glucose ...
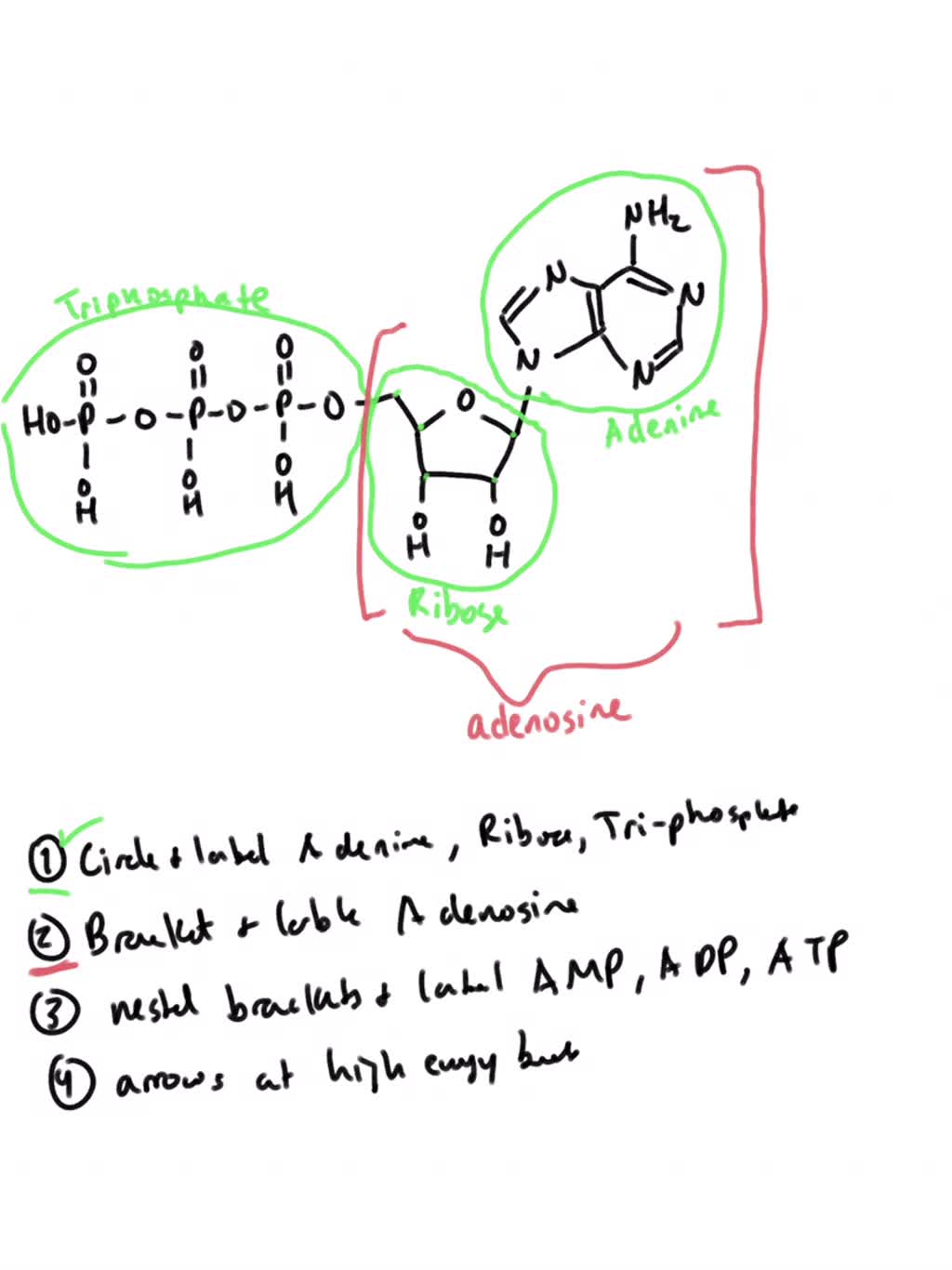
Draw the chemical structure of ATP, 1. Circle and label the following parts: Adenine, Ribose,, Tri-Phosphate., 2. Put a bracket around and label the part that is called, Adenosine., 3. Use nested ...













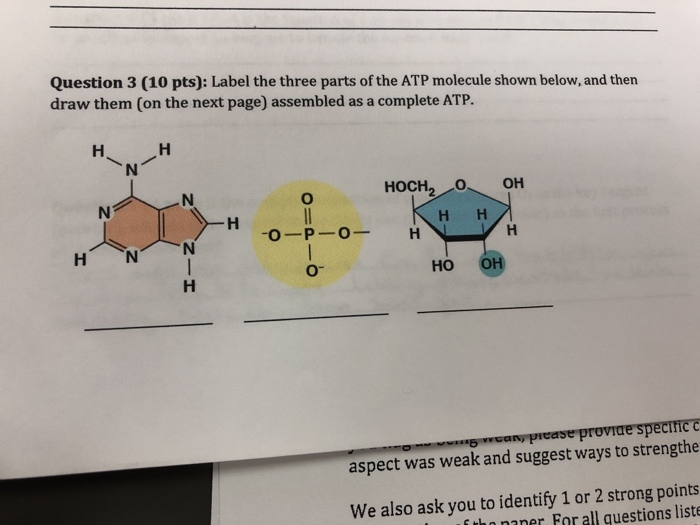
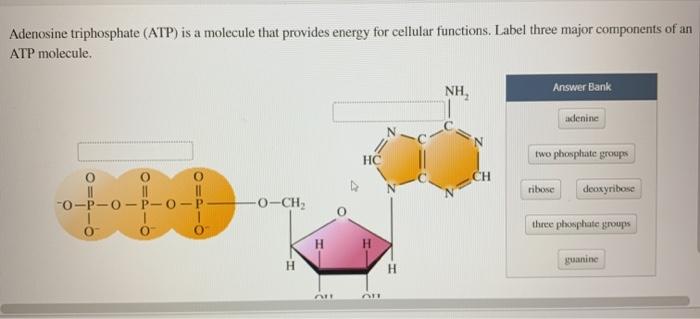



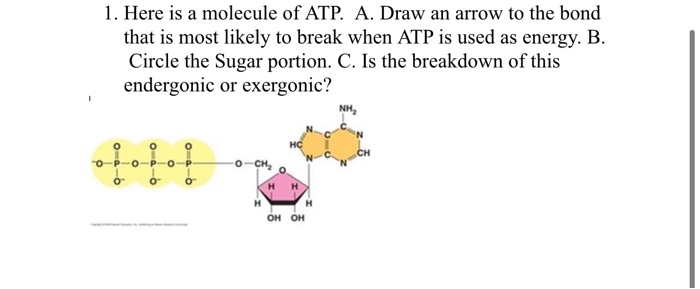


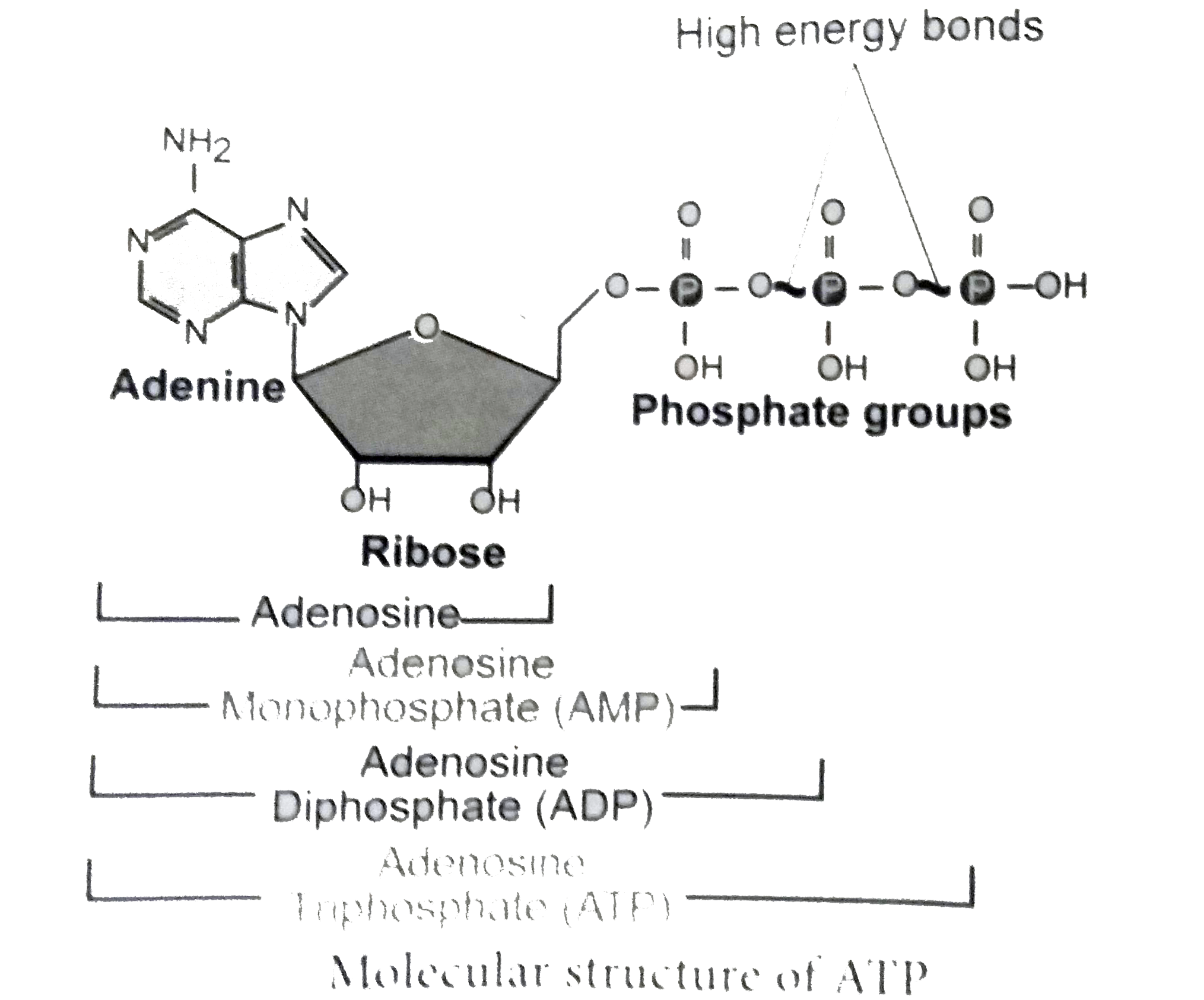




Post a Comment for "38 draw and label an atp molecule"