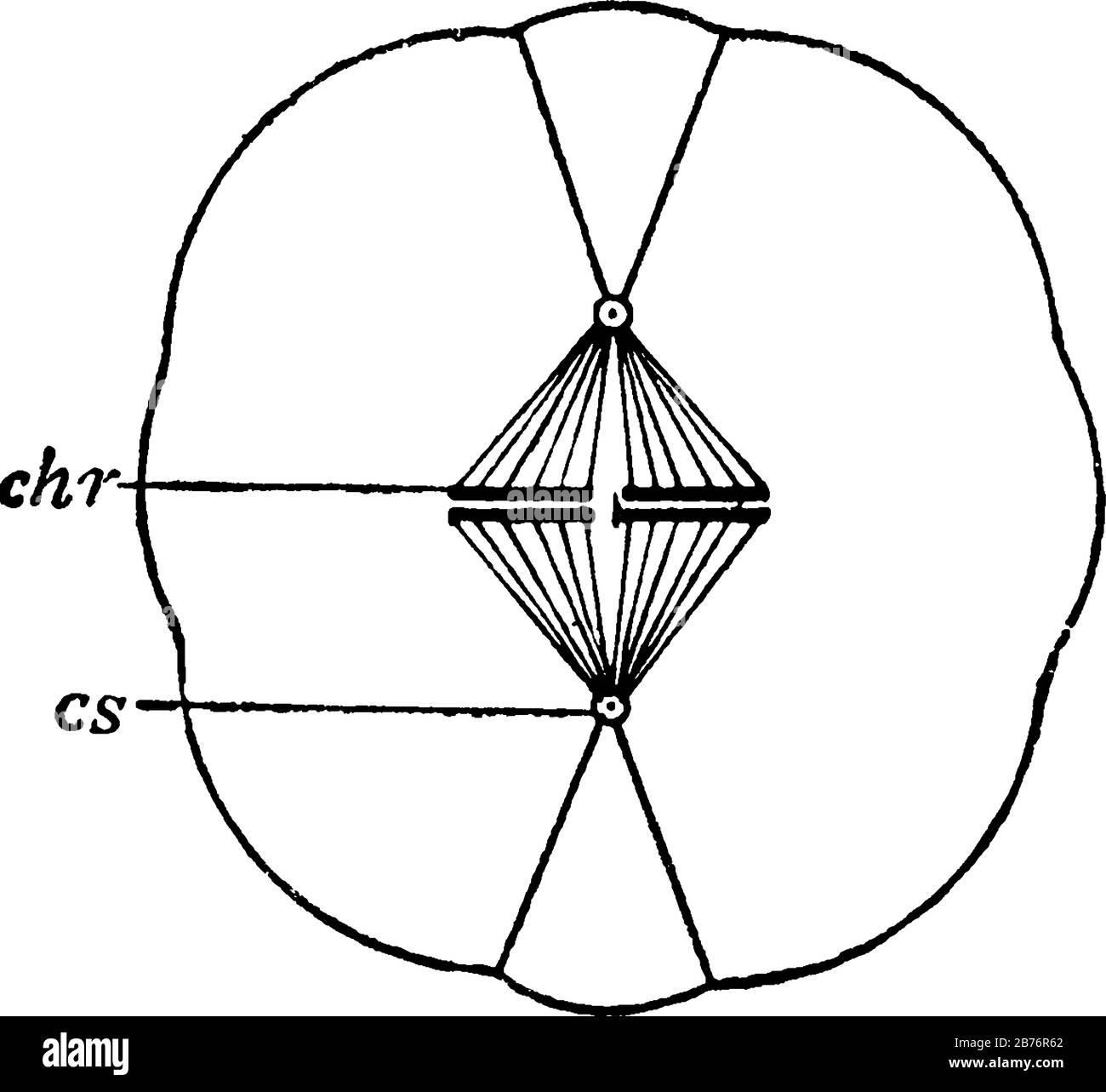
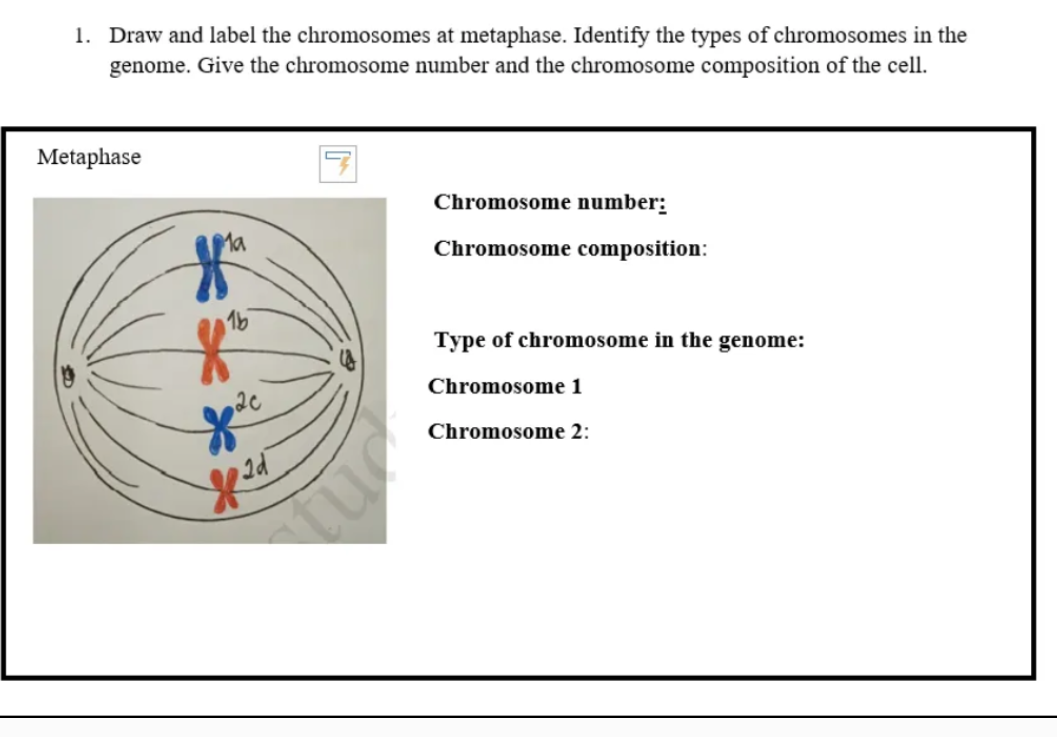
38 sketch of chromosome and label the telomeres
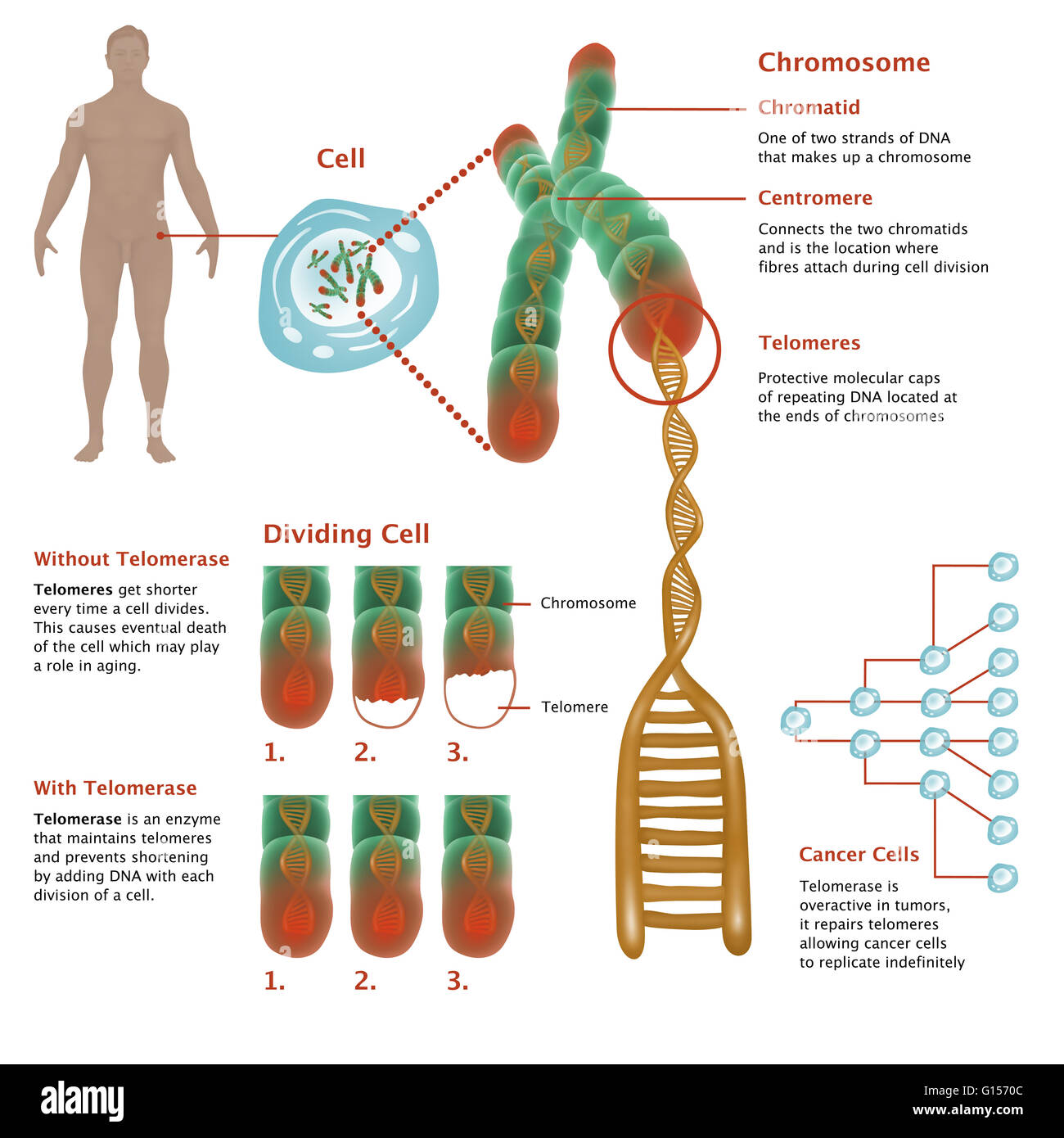
Telophase - Definition and Stages in Mitosis and ... - Biology Dictionary Telophase is the final stage in cell division. During telophase, the nuclear envelopes reform around the new nuclei in each half of the dividing cell. The nucleolus, or ribosome producing portions of the nucleus return. As the cell has finished moving the chromosomes, the main parts of the spindle apparatus fall depolymerize, or fall apart. PDF Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance 35. Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the telomeres. 36. Explain telomere erosion and the role of telomerase. 37. Why are cancer cells immortal, but most body cells have a limited life span? 16.3 A chromosome consists of a DNA molecule packed together with proteins 38.
PDF Leology - Welcome How is it repaired? linking 4-hym.ne Oases adjacen+,whrch interference replica HT. to Pepcarecl repair enzgmeJ Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the telomeres. Explain telomere erosion and the role of telomerase. each ce repbrahcn„+he st-y-anð as shcí+er. Tetcmerose cco-algzes lem4hening Çelcmeres 9errn Copyr6ht 2010 Pearson

Sketch of chromosome and label the telomeres
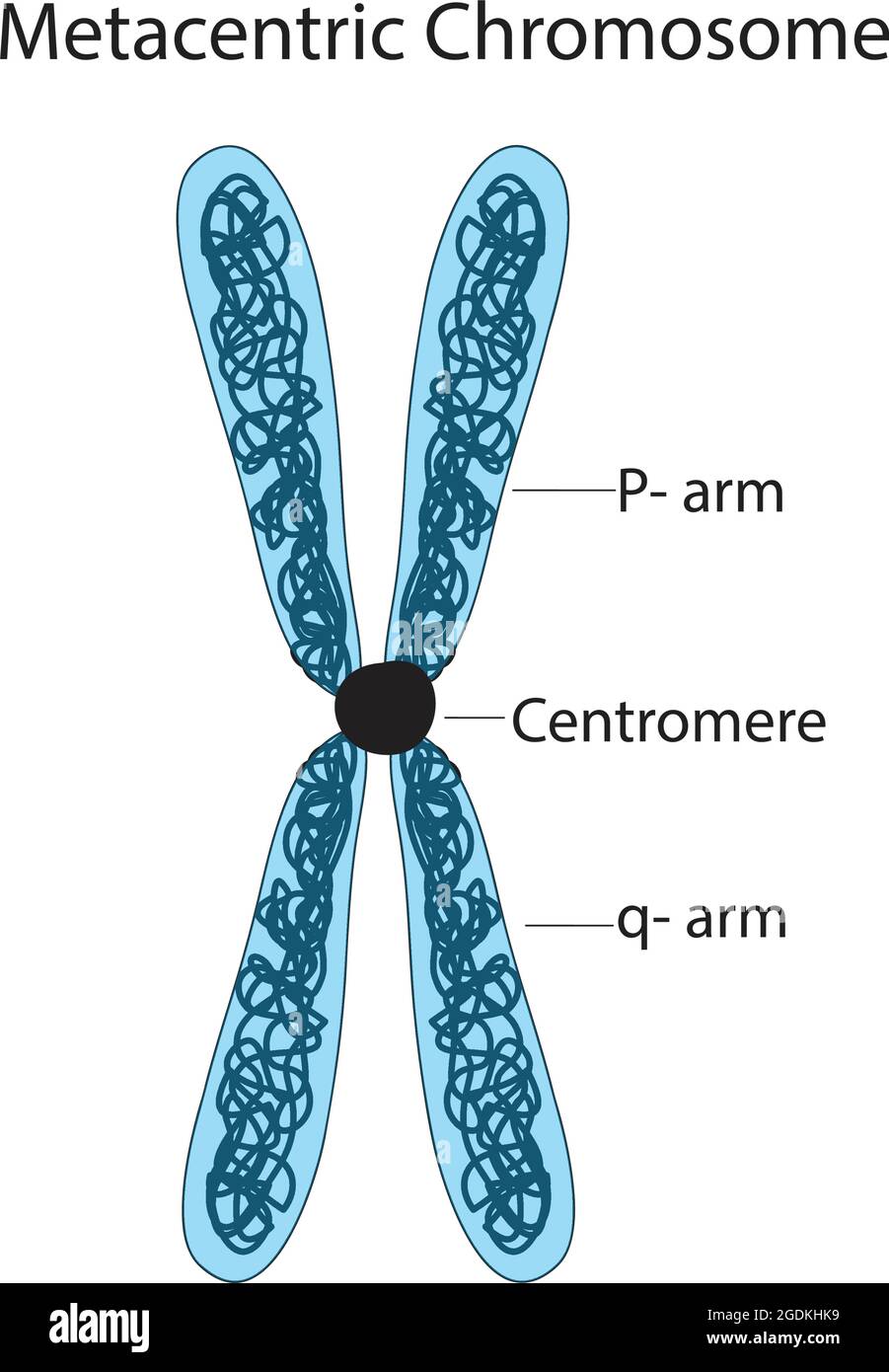
student_handout_in_word.docx - Select a chromosome from ... - Course Hero Confirm that the colors of the chromosomes and the board match. Select a chromosome decal from the cryostorage area of the board and sketch it on your Cytogenetics Report, noting the centromere, telomere, and p and q arms. Note the centromere position as well. Read the case study found on the left side of the board. PDF DNA STRUCTURE AND R BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA - Weebly c. Sketch a T2 bacteriophage and label the parts listed in b d. What effect does the T2 phage have one E. coli? ... Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the telomeres. Evolution Activity #2 Page 12 of 12 26. Explain telomere erosion and the role of telomerase. ... Telomere - Genome.gov A telomere is a region of repetitive DNA sequences at the end of a chromosome. Telomeres protect the ends of chromosomes from becoming frayed or tangled. Each time a cell divides, the telomeres become slightly shorter. Eventually, they become so short that the cell can no longer divide successfully, and the cell dies. Human Cell 3-D.
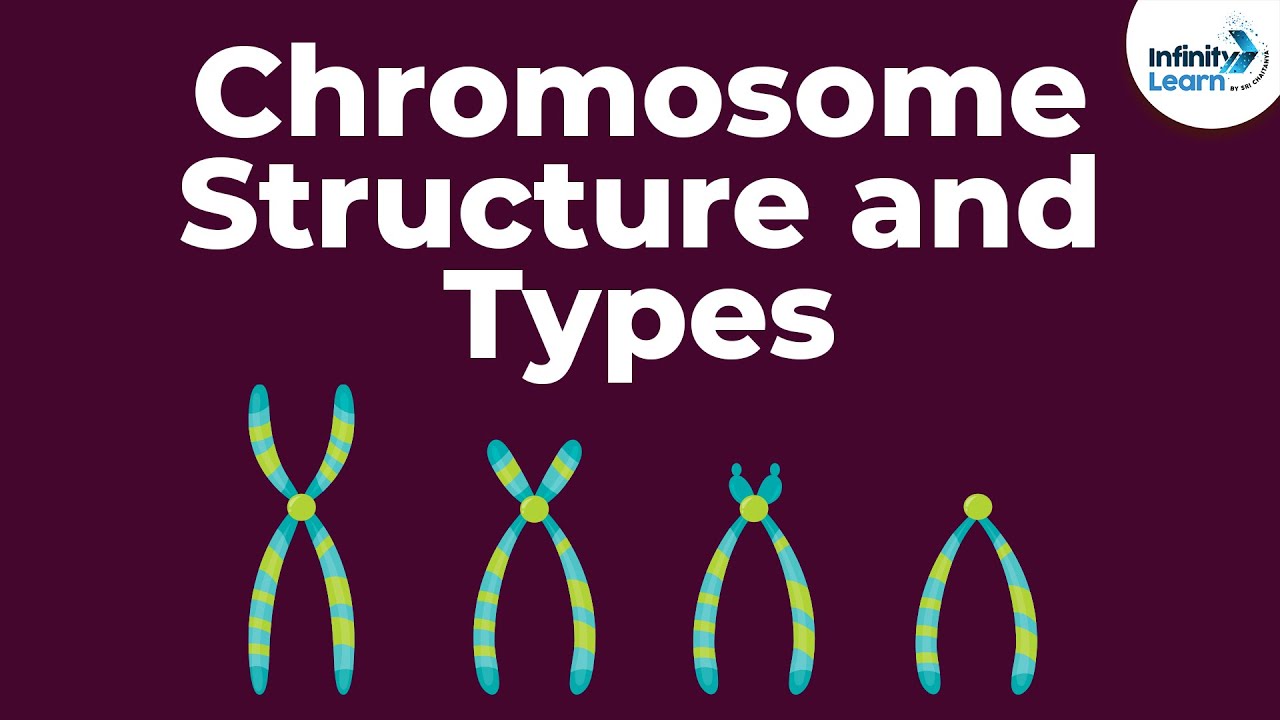
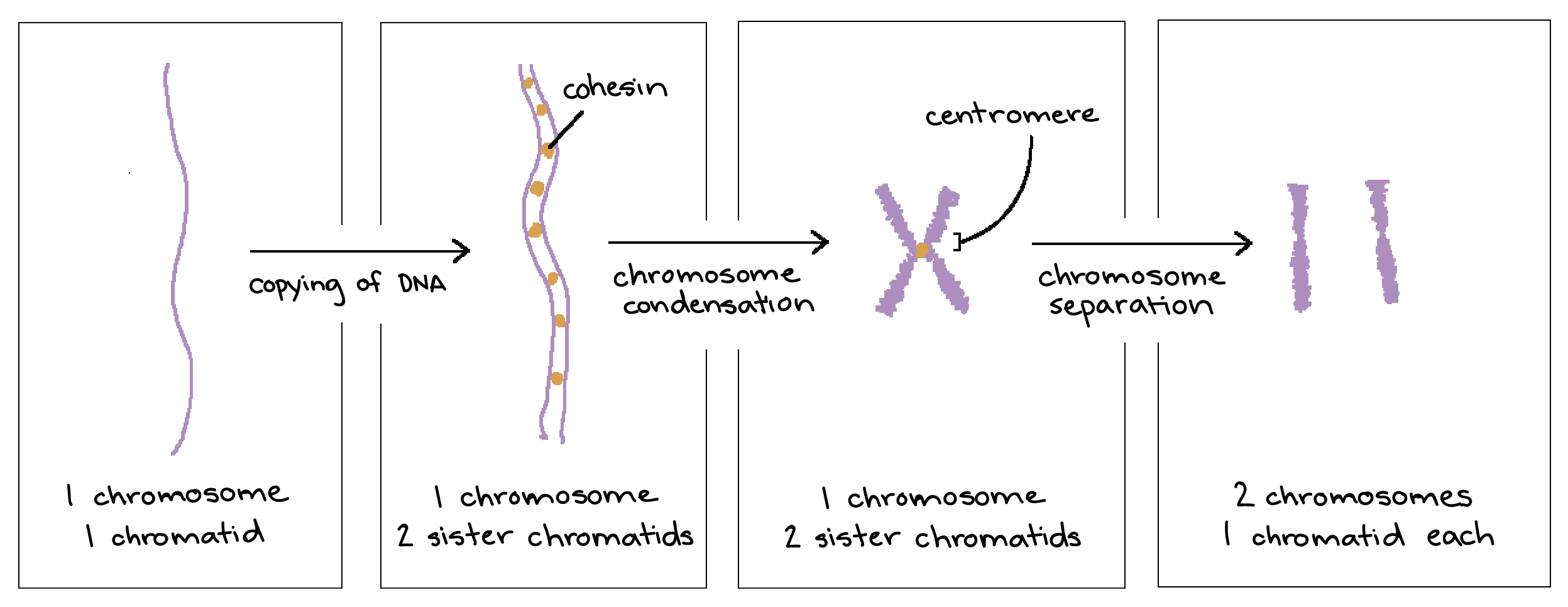
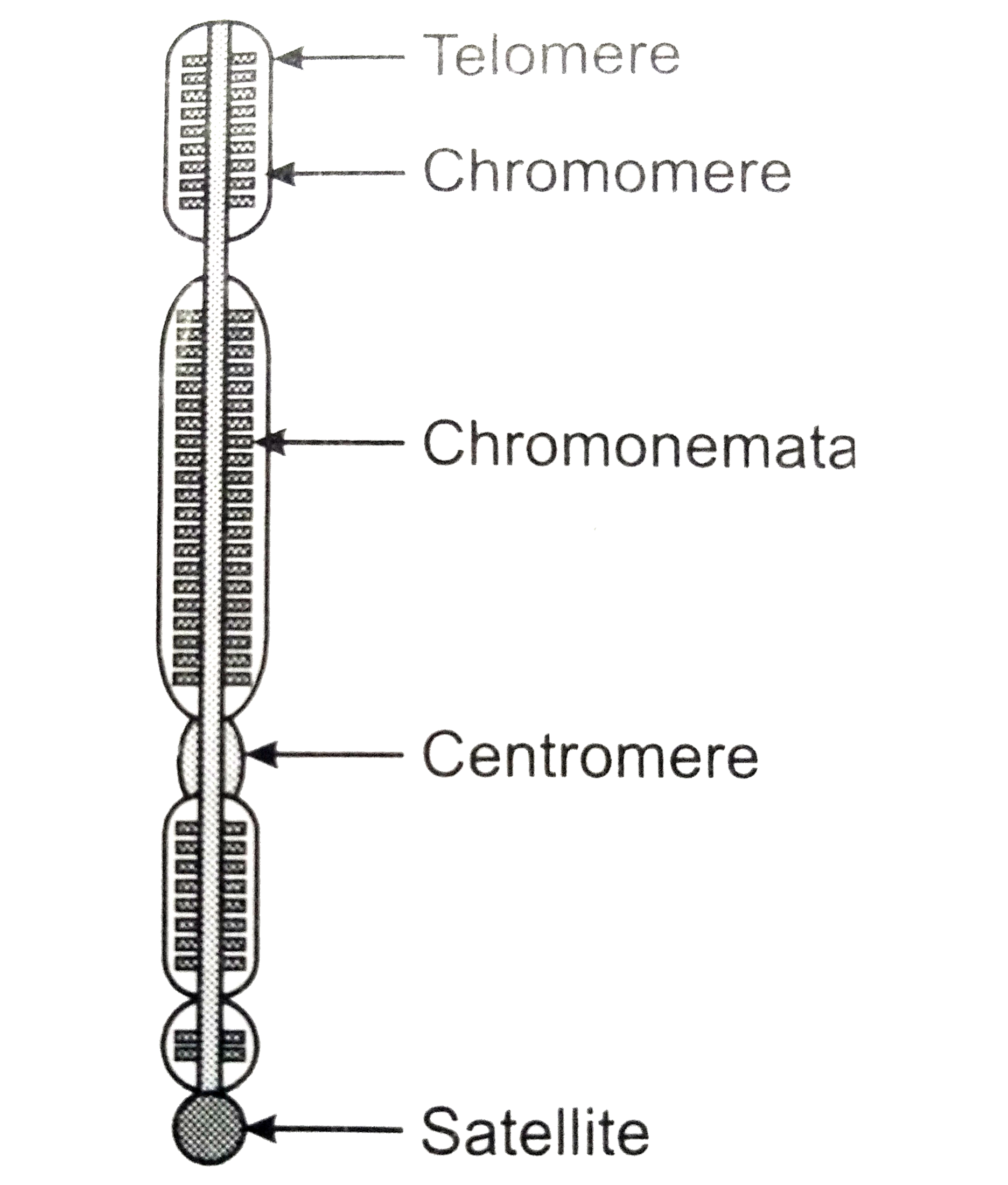
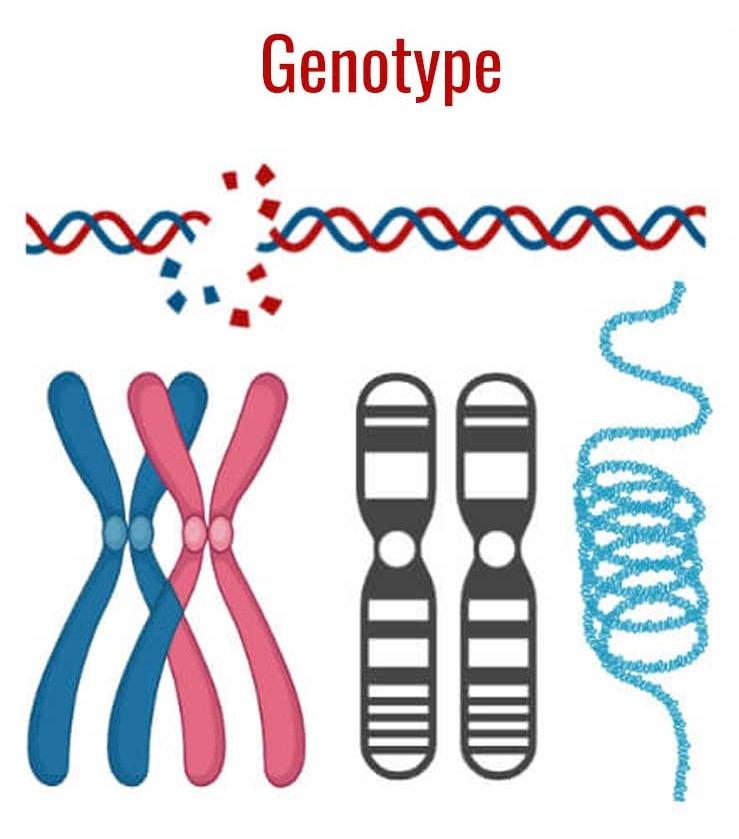
Sketch of chromosome and label the telomeres. Chromosome - Definition, Function & Structure | Biology Dictionary Chromosome Definition. A chromosome is a string of DNA wrapped around associated proteins that give the connected nucleic acid bases a structure. During interphase of the cell cycle, the chromosome exists in a loose structure, so proteins can be translated from the DNA and the DNA can be replicated.During mitosis and meiosis, the chromosome becomes condensed, to be organized and separated. Chromosome Structure: Definition, Function and Examples A chromosome has generally 8 parts; Centromere or primary constriction or kinetochore, chromatids, chromatin, secondary constriction, telomere, chromomere, chromonema, and matrix. Centromere or Kinetochore: It is the primary constriction at the center to which the chromatids or spindle fibers are attached. Chromosome: its Parts, Functions and Types (1934 Words) | Biology Telomeres contain the ends of the long linear DNA molecule contained in each chromatid. The general morphology of a set of chromosomes or karyotype, of an individual depends upon the dimensions of the chromosomes, position of the kinetochores, (centromeres) and the presence of secondary constrictions and satellite bodies. Solved Sketch a duplicated chromosome and label the sister | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Sketch a duplicated chromosome and label the sister chromatids, the centromere, and the kinetochor4es. What are the functions of centromeres and of Kinetochores? 2. Assume that an animal has a diploid chromosome number of ten. (a) How many chromosomes would it have in a typical body cell, such as a sking cell?
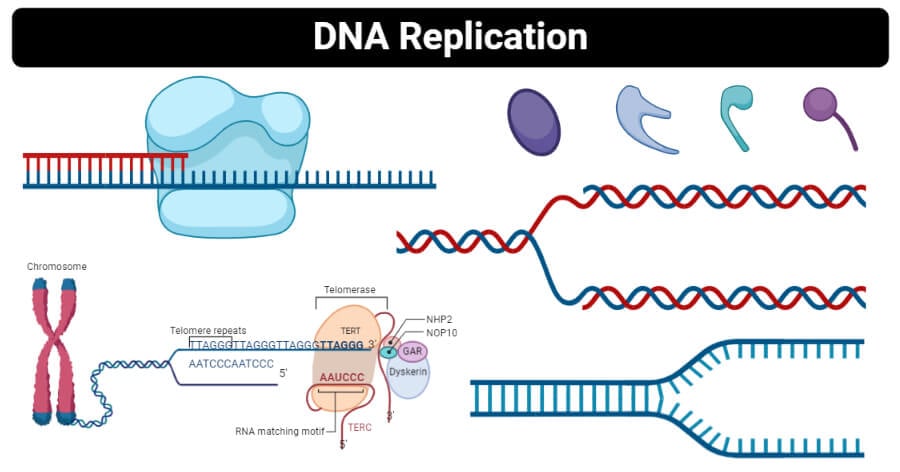
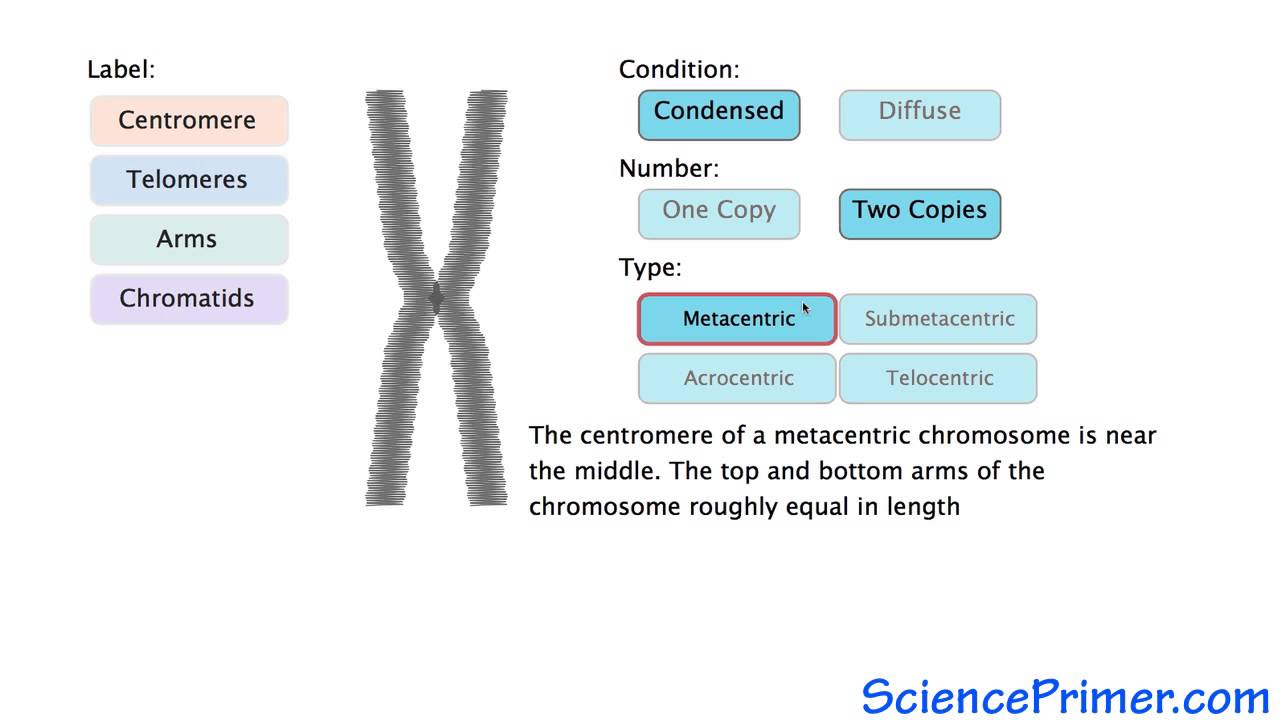
PDF hssb0502t tx studygda - Weebly 4. Make a sketch of how DNA goes from a long stringy form to a tightly condensed form. On the final stage (the condensed, duplicated chromosome), label the chromatid, telomere, and centromere. chromosome centromere anaphase histone telomere telophase chromatin prophase chromatid metaphase Youreka Science: The Discovery of Telomerase: The Key to Chromosome ... 00:05:12.28 By discovering that telomerase. 00:05:14.28 is the enzyme that can extend the protective caps. 00:05:16.29 at the ends of chromosomes, called the telomere, 00:05:19.28 these scientists solved one of the most important puzzles in biology. 00:05:25.08 How is our DNA being protected from degradation. Telomeres of Human Chromosomes | Learn Science at Scitable Human telomeres are comprised of a 230-kb array of duplex TTAGGG repeats, ending in a 100 to 200 nucleotide protrusion of single-stranded TTAGGG repeats. This DNA can exist as a t-loop in which ... Meiosis Flashcards | Quizlet Draw a picture of a replicated chromosome. Label the sister chromatids and the centromere. Draw a picture of a non-replicated chromosome. How do they differ? ... replicated homologous chromosomes pair together. Crossing over happens. Pairs of homologous chromosomes line up in the center and are separated into 2 haploid cells. Describe what ...
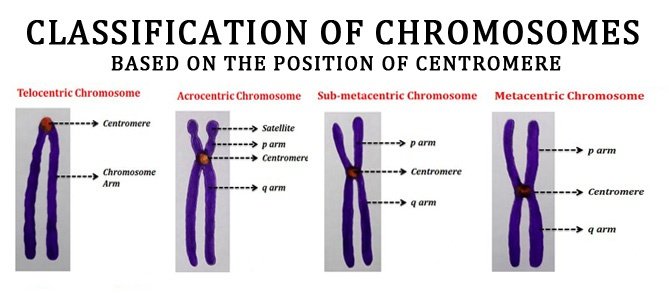
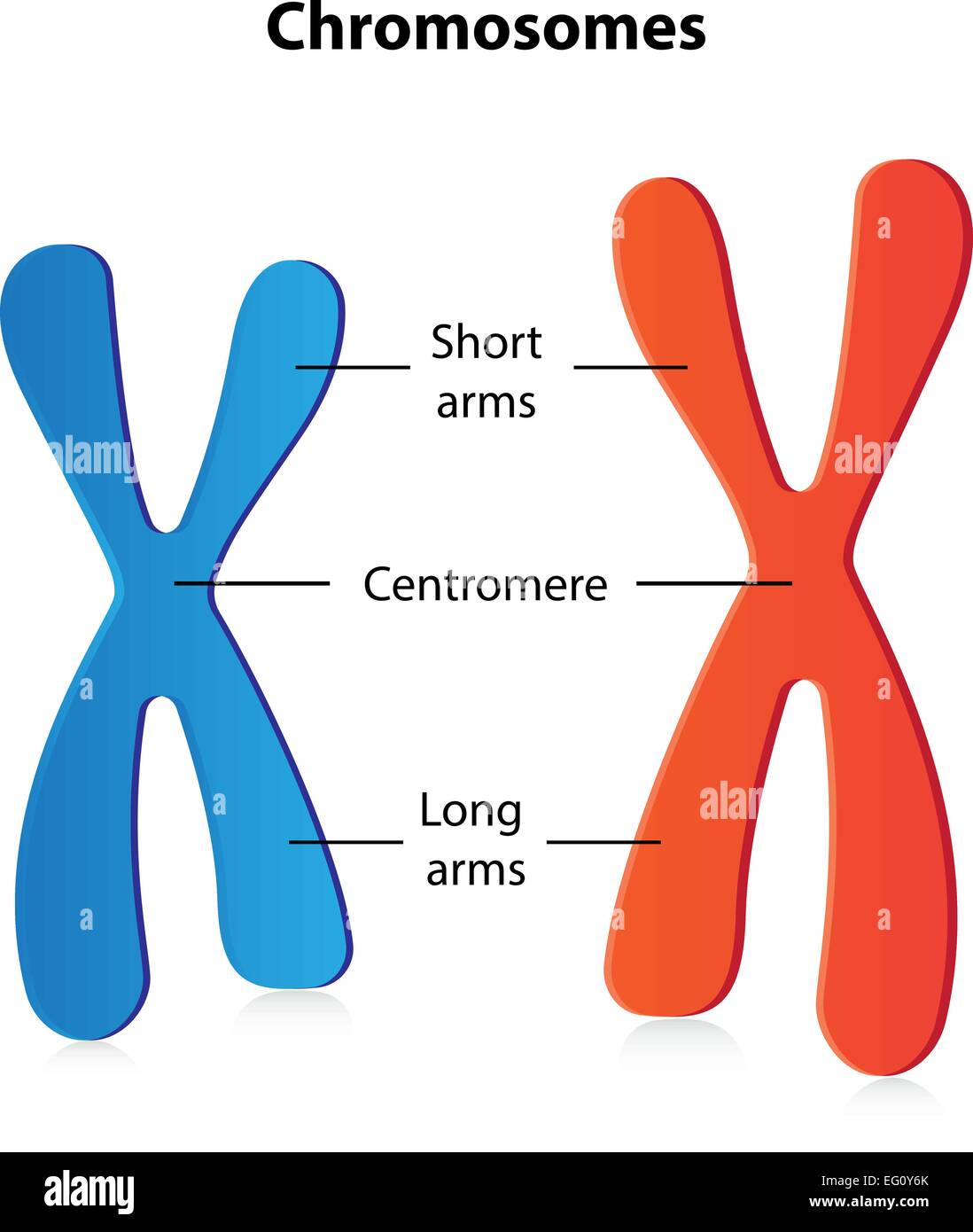
Diagram of Chromosome Structure - Online Biology Dictionary The name chromosome, meaning "colored body," is derived from the fact that in early studies of cellular structure the chromosomes could be easily stained with colored dyes and therefore showed up as colored bodies under the microscope. The diagram of chromosome structure above shows how DNA is organized in a eukaryotic cell. Draw the structure of the chromosome and label its parts. > Telomeres: Telomeres are repetitive stretches of DNA located at the ends of linear chromosomes. They protect the ends of chromosomes. At the tip of every chromosome could be a repetitive nucleotide sequence cap called a telomere. Arranged on the chromosomes are genes. Genes are products of DNA and contain the instructions for building proteins. Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Quia Sketch a T2 bacteriophage and label its head, tail sheath, tail fiber, and DNA. 9. ... 37. Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the . telomeres. 38. Explain telomere erosion and the role of . telomerase. MLA CE Course Manual: Molecular Biology Information Resources (Genetics ... Each chromosome arm is divided into regions, or cytogenetic bands, that can be seen using a microscope and special stains. The cytogenetic bands are labeled p1, p2, p3, q1, q2, q3, etc., counting from the centromere out toward the telomeres. At higher resolutions, sub-bands can be seen within the bands.
(PDF) Quantitative Dynamics of Telomere Bouquet Formation Sketch of a wheat spike, showing spikelets, florets and anthers. Each anther contains four locules. ... It would be interesting to label. individual chromosome telomeres to determine which of these.
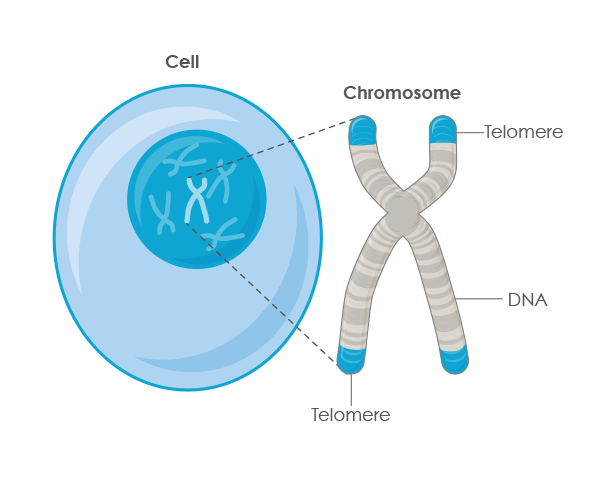
Chromosomes Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Telomeres are repetitive stretches of DNA located at the ends of linear chromosomes. They protect the ends of chromosomes in a manner similar to the way the tips of shoelaces keep them from unraveling. In many types of cells, telomeres lose a bit of their DNA every time a cell divides.
Chromosomes (article) | Cell cycle | Khan Academy The 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the X and Y chromosomes; see below). Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid ( 1n ).
PDF SECTION THE CELL CYCLE 5.1 Study Guide Label each step and list the major events ... Refer to Figure 5.5 to sketch how DNA goes from a long stringy form to a tightly condensed form. Label the parts of the condensed, duplicated chromosome. MAIN IDEA: ... Telomeres help prevent chromosomes from sticking to each other.
DOCX Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Ms Beland's Classes Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the . telomeres. Explain telomere erosion and the role of . telomerase. Why are cancer cells immortal, but most body cells have a limited life span? Concept 16.3 A chromosome consists of a DNA molecule packed together with proteins .
Mitosis and Cell Cycle Study - PHDessay.com The suffix -tin indicates that something is stretched and thin. Is the loose combination of DNA and proteins that looks sort of like spaghetti. Sister chromatids are held together at the which looks pinched. The ends of DNA molecules form structures called that help prevent the loss of genes. Regulation of the Cell Cycle Study Guide
Chromosome Structure (Labeling) - The Biology Corner This simple worksheet shows a diagram of a chromosome and where it is located in the nucleus of the cell. Students use a word bank to label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, DNA, and nucleus. This worksheet was created for introductory biology for students to practice labeling the parts of a chromosome. Grade Level: 6-12
Unit 7: Chromosomes & Cell Division Flashcards - Quizlet Mitosis is the nucleus dividing ( Mitosis----> Nucleus Dividing ) Cytokinesis is the cytoplasm dividing ( Cytokinesis-----> Cytoplasm Dividing ) What are the 4 stages of mitosis? Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. Draw a picture of prophase and label centrioles, spindles, nuclear membrane, and chromosomes.
PDF Chapter 13 Active Reading Guide - Woodstown-Pilesgrove Regional School ... 35. Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the telomeres. 36. Explain telomere erosion and the role of telomerase. 37. Why are cancer cells immortal even though most body cells have a limited life span? 38. Explain the roles of each of the following enzymes in DNA proofreading and repair. a. DNA polymerase _____
6 Main Parts of a Chromosome - Biology Discussion The chromosome with a satellite is referred to as 'SAT-chromosome'. There are at-least two SAT-chromosomes in each diploid nucleus. Many polyploid species, however, have only two SAT-chromosomes. For example, hexaploids wheat. Part # 6. Telomere: The tips or the terminal ends of chromosomes are called telomeres.
Telomere - Genome.gov A telomere is a region of repetitive DNA sequences at the end of a chromosome. Telomeres protect the ends of chromosomes from becoming frayed or tangled. Each time a cell divides, the telomeres become slightly shorter. Eventually, they become so short that the cell can no longer divide successfully, and the cell dies. Human Cell 3-D.
PDF DNA STRUCTURE AND R BUILDING BLOCKS OF DNA - Weebly c. Sketch a T2 bacteriophage and label the parts listed in b d. What effect does the T2 phage have one E. coli? ... Make a sketch of a chromosome and label the telomeres. Evolution Activity #2 Page 12 of 12 26. Explain telomere erosion and the role of telomerase. ...
student_handout_in_word.docx - Select a chromosome from ... - Course Hero Confirm that the colors of the chromosomes and the board match. Select a chromosome decal from the cryostorage area of the board and sketch it on your Cytogenetics Report, noting the centromere, telomere, and p and q arms. Note the centromere position as well. Read the case study found on the left side of the board.














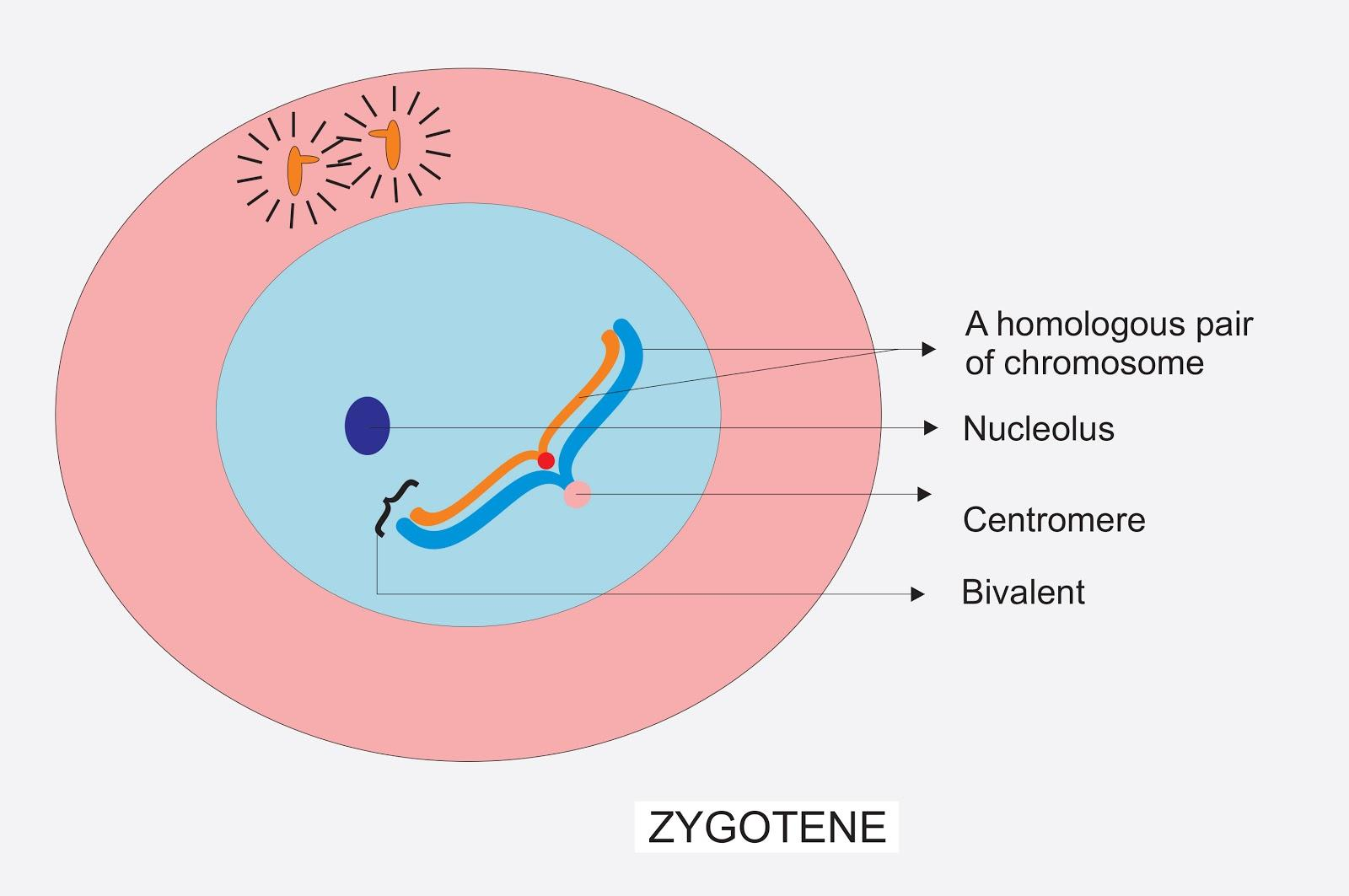





Post a Comment for "38 sketch of chromosome and label the telomeres"