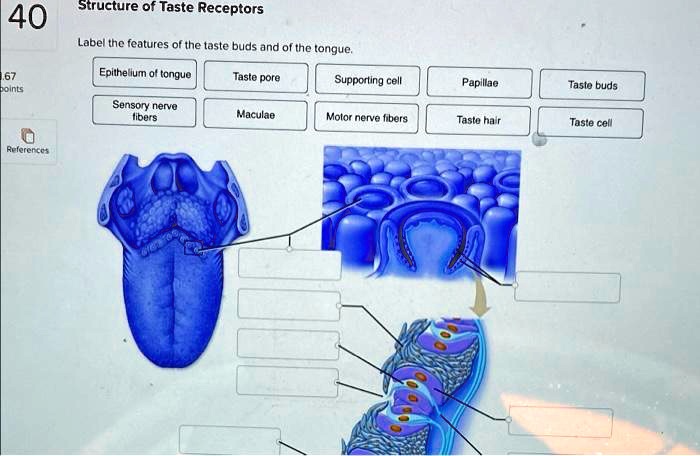
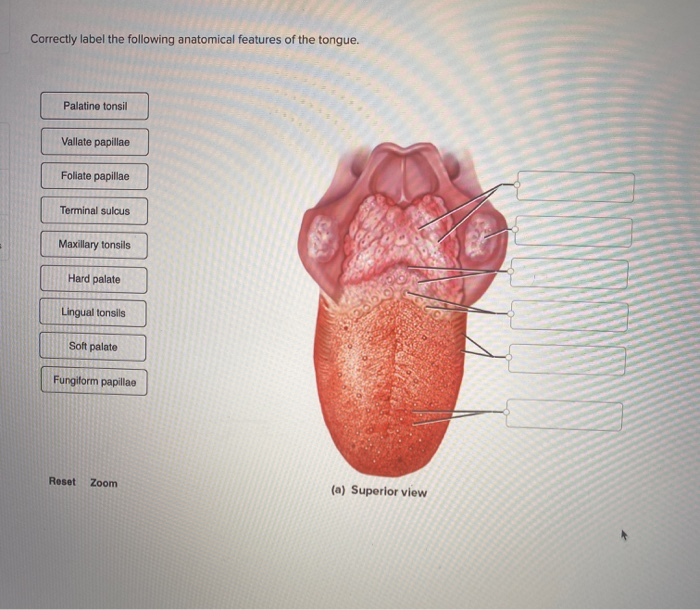
39 label of tongue
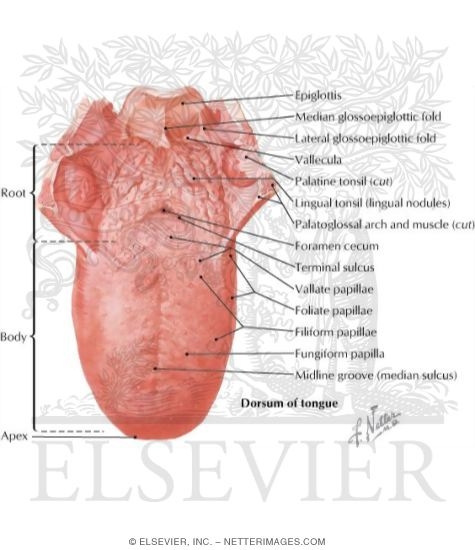
Tongue | Anatomy, Parts, Pictures, Diagram of Human Tongue Parts of the Tongue The top of the tongue (superior surface) has a V-shaped line known as the terminal sulcus that divides the tongue into the anterior and posterior surfaces. The anterior surface is made up of the apex at the tip and body. The posterior surface is made up entirely of the root. Tongue: Anatomy, muscles, neurovasculature and histology | Kenhub Anatomy. Under normal circumstances, the tongue is a pink, muscular organ located within the oral cavity proper. It is kept moist by the products of the major and minor salivary glands, which aids the organ as it facilitates deglutition, speech, and gustatory perception.While there is significant variability in the length of the tongue among individuals, on average, the organ is roughly 10 cm ...
Tongue: Definition, Location, Anatomy & Function - Cleveland Clinic If your tongue is discolored, it could be a sign of an underlying problem. White tongue: White patches on your tongue could indicate thrush, lichen planus, leukoplakia or other conditions. Red or purple tongue: If your tongue is red or purple in color, it could be related to harmless conditions like geographic tongue.
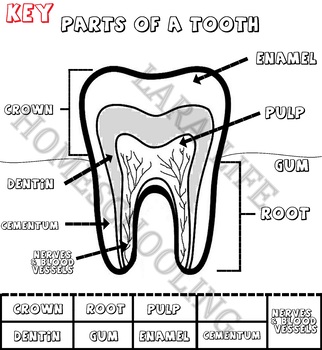
Label of tongue
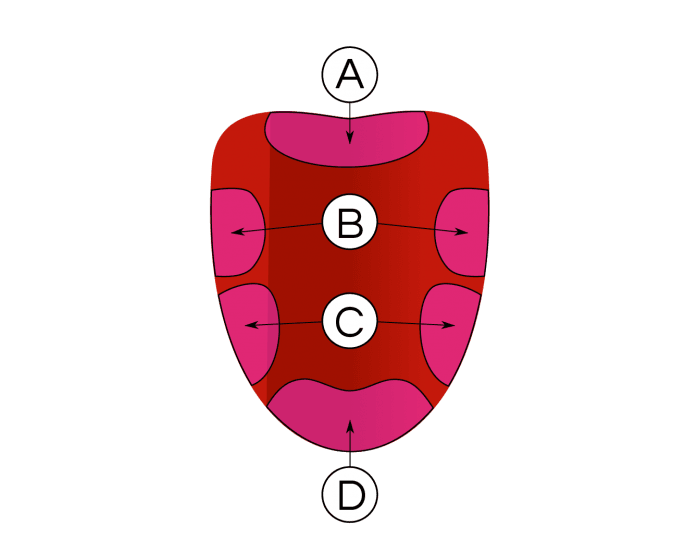
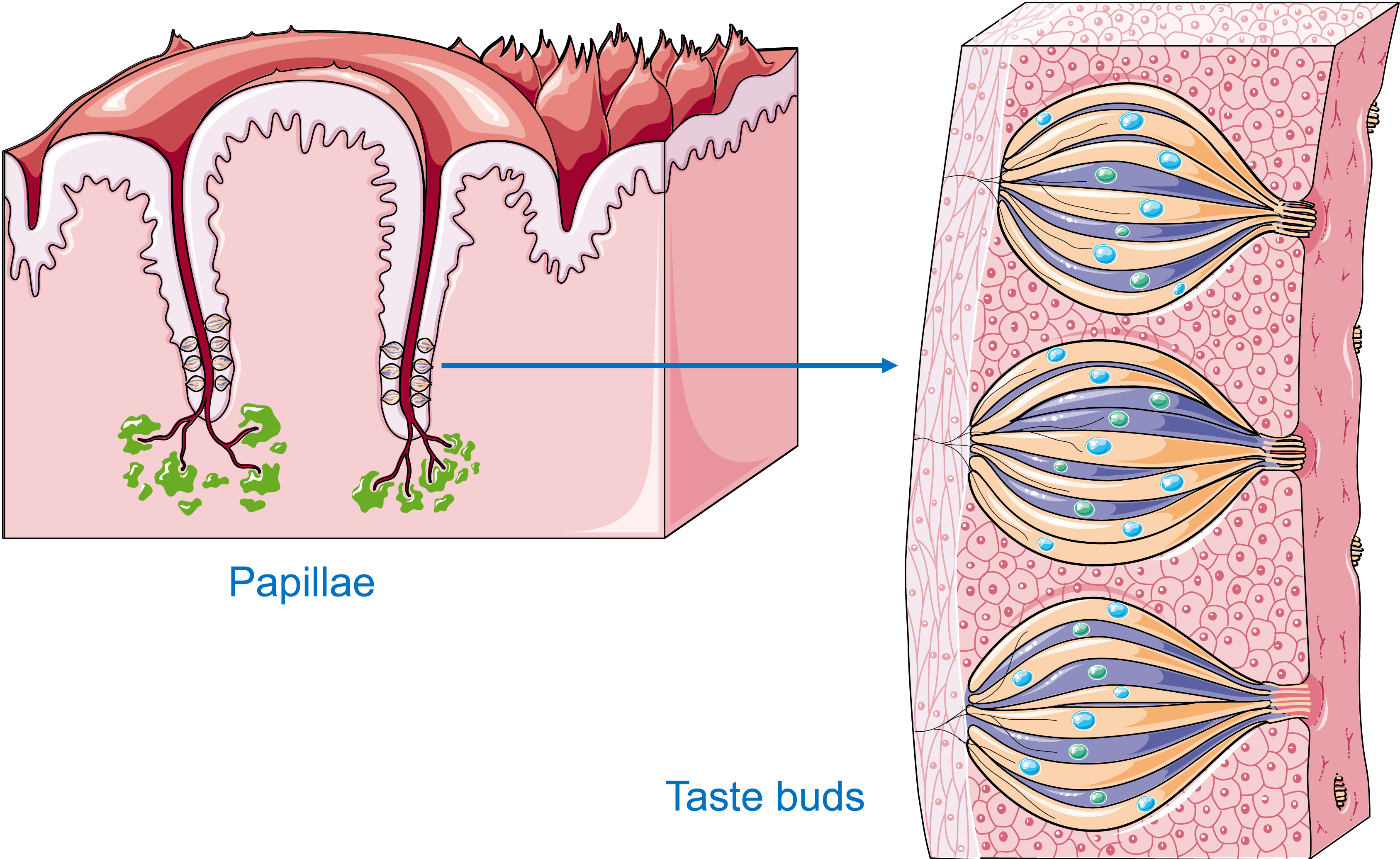
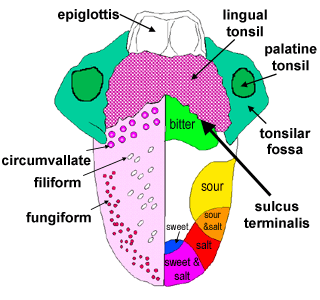
Geographic tongue - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Signs and symptoms of geographic tongue may include: Smooth, red, irregularly shaped patches (lesions) on the top or side of your tongue. Frequent changes in the location, size and shape of lesions. Discomfort, pain or burning sensation in some cases, most often related to eating spicy or acidic foods. Many people with geographic tongue have no ... taste (tongue labeling) Diagram | Quizlet Definition (least numerous) taste buds arranged in V formation on posterior surface of the tongue, cup shaped Location basic tastes sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami sweet respond to sugar (fructose, sucrose, glucose), saccharine, some lead salts, and some amino acids, alcoholk salty due to influx of metal ions particularly sodium sour Taste Buds: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment - Verywell Health There are four types of papillae: Filiform: The most common, covering the tough surface of the tongue, and do not contain taste buds Fungiform: Located near the front of the tongue Circumvallate: Located near the back of the tongue Foliate: Located on the sides of the tongue
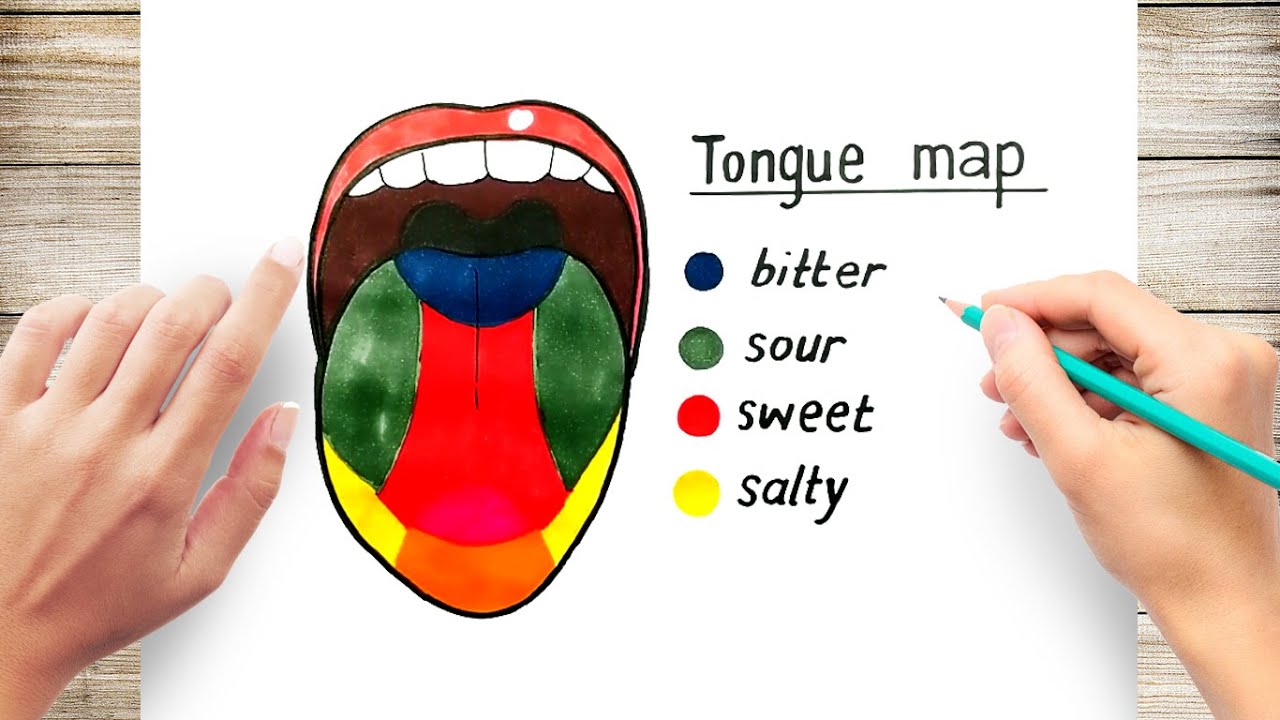
Label of tongue. 23.3 The Mouth, Pharynx, and Esophagus - OpenStax The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity). The structures of the mouth are illustrated in Figure 23.7. At the entrance to the mouth are the lips, or labia (singular = labium). Their outer covering is skin, which transitions to a mucous membrane in the mouth proper. label the tongue Quiz - PurposeGames.com This is an online quiz called label the tongue. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Popular Today. Cities of South West Asia. Colours in German. New York City: Boroughs and Waterways. Easy Earth's Rotation/Revolution. Polygons 3-sided to 14-sided. The Taste Map of the Tongue You Learned in School Is All Wrong Sweet in the front, salty and sour on the sides and bitter at the back. It's possibly the most recognizable symbol in the study of taste, but it's wrong. In fact, it was debunked by chemosensory... Taste buds: anatomy and function. | Kenhub Taste buds are microscopic sensory organs containing chemosensory cells which synapse with afferent fibers of gustatory nerves. The number of taste buds in the oral cavity and uppermost gastrointestinal tract is subject to a high degree of interindividual variation (500-5000) while the number of cells in one taste bud can be up to 150. Due to the abrasive environment of the oral cavity ...
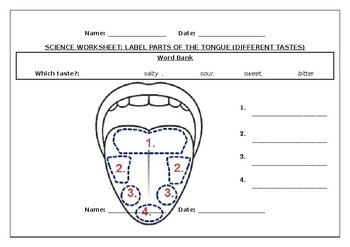
Human Tongue Diagram - BYJU'S The human tongue can be distinguished into three segments: the base, body, tip, or apex. The apex is present immediately behind the incisor teeth and is considered a mobile aspect of the tongue. It is followed by the body, which has rough superior and smooth inferior surfaces. The body is populated with three types of lingual papillae. Label the tongue - Liveworksheets Label the tongue Label the parts of the tongue ID: 1727488 Language: English School subject: Science Grade/level: 4 Age: 6-10 Main content: Label the parts of the tongue Other contents: Add to my workbooks (26) Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Tongue Diagram with Detailed Illustrations and Clear Labels - BYJU'S The tongue is an organ responsible for the manipulation of food during the process of chewing (also called mastication). Moreover, it is also responsible for the sensation of taste (along with the nose). Hence, you cannot taste or smell food when you have a fever or cold. Tongue: Anatomy, Function, and Disorders - Verywell Health The visible parts of the tongue include: Root: This is most often defined as the back third of the tongue. It sits low in the mouth and near the throat, and it is relatively fixed in place. It is attached to the hyoid bone and mandible (lower jaw). It is close in proximity to two muscles: the geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles.
Tongue Structure - Parts and Functions of Tongue - BYJU'S The tongue is made up of three elements: Epithelium Muscles Glands Epithelium The epithelium comprises papillae and taste buds. The taste buds help to sense taste. They are lined by squamous epithelial tissue and have a broad bottom. The taste cells are slender, rod-shaped with a nucleus in the centre. The free surface comprises short taste hair. Picture of the Tongue - WebMD The tongue is covered with moist, pink tissue called mucosa. Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its rough texture. Thousands of taste buds cover the surfaces of the papillae. Taste buds... Pictures: What Your Tongue Says About Your Health - WebMD A tongue without any small bumps on the top may look glossy red. You may get it if you don't get enough of some nutrients like iron, folic acid, or B vitamins. Infections, celiac disease, or some... Label Tongue Taste Areas Printout - EnchantedLearning.com The tongue is a strong muscle in the mouth that is covered with papillae (small bumps on the tongue) and taste buds (that sense bitter, salty, sweet, and sour tastes). The taste buds are clustered along the sides of the tongue. Read the descriptions, then label the tongue below. bitter - Bitter tastes (like the taste of tonic water) are mostly ...
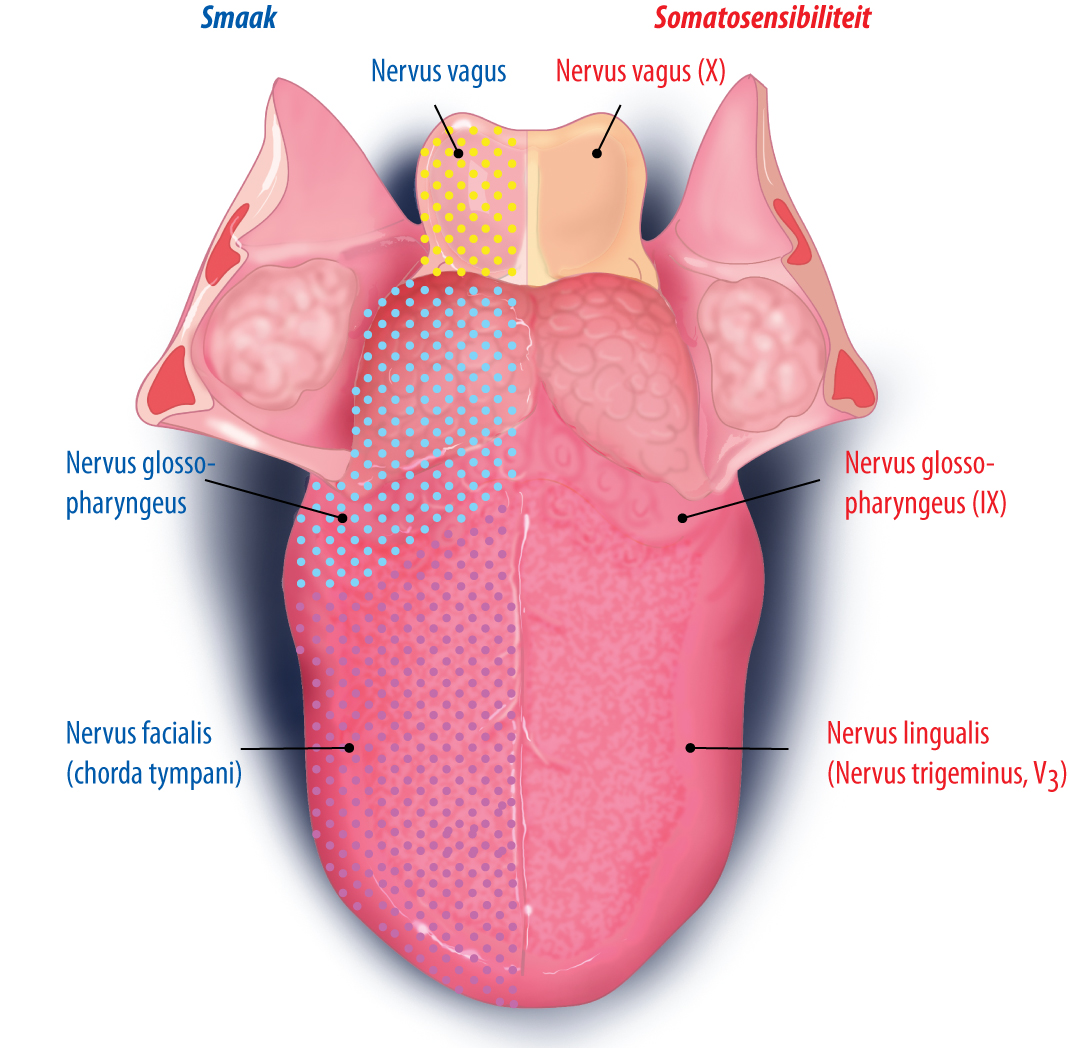
The Tongue - Muscles - Innervation - Vasculature - TeachMeAnatomy Extrinsic Muscles. The extrinsic muscles of the tongue originate from structures outside the tongue and insert onto it.. They are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve - with the exception of the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve.. Genioglossus. The genioglossus muscle is a large, thick muscle, which contributes significantly to the shape of the tongue.
Taste Buds: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment - Verywell Health There are four types of papillae: Filiform: The most common, covering the tough surface of the tongue, and do not contain taste buds Fungiform: Located near the front of the tongue Circumvallate: Located near the back of the tongue Foliate: Located on the sides of the tongue
taste (tongue labeling) Diagram | Quizlet Definition (least numerous) taste buds arranged in V formation on posterior surface of the tongue, cup shaped Location basic tastes sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami sweet respond to sugar (fructose, sucrose, glucose), saccharine, some lead salts, and some amino acids, alcoholk salty due to influx of metal ions particularly sodium sour
Geographic tongue - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic Signs and symptoms of geographic tongue may include: Smooth, red, irregularly shaped patches (lesions) on the top or side of your tongue. Frequent changes in the location, size and shape of lesions. Discomfort, pain or burning sensation in some cases, most often related to eating spicy or acidic foods. Many people with geographic tongue have no ...








:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/papillae-foliatae/w69KGkItSL6yEprgTgA_Papillae_foliatae_01.png)



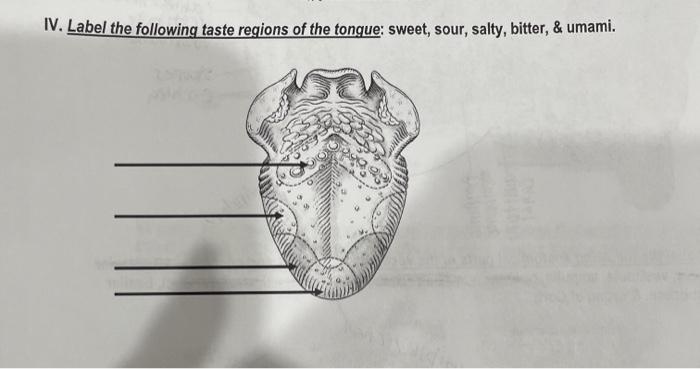












Post a Comment for "39 label of tongue"