44 two step reaction diagram
Answered: Sketch an energy diagram for a two-step… | bartleby To draw: An energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which both steps are exergonic and in which the second step has a higher-energy transition state than the first. Label the parts of the diagram correspoding to reactant, product, intermediate, overall ΔG‡, and overall ΔG°. arrow_forward CH 368: Unit 2 - University of Texas at Austin Reaction Path Diagrams. Reaction path diagrams, as represented above, are a two dimensional slice of a multidimensional energy surface for the reaction. Conventionally, they are a plot of energy (in the rigorous case, free energy, G) versus the reaction coordinate. 6. Reaction Mechanism.
Answered: Draw a reaction energy diagram for a… | bartleby Draw a reaction energy diagram for a two-step exothermic reaction whose second step is faster than. the first step. Label the intermediate, transition states, ΔH, and activation energies. check_circle.
Two step reaction diagram
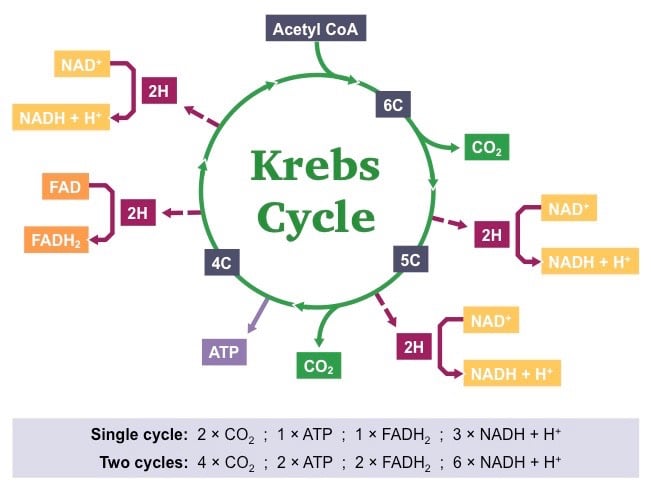
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction (heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram. 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax The catalyzed reaction is the one with lesser activation energy, in this case represented by diagram b. Check Your Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step. 7 Krebs Cycle Steps and Process: Diagram, Explanation Therefore, it is a two-step reaction sequence. The Krebs cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration. During the Krebs cycle, energy stored in pyruvate is transferred to NADH and FADH 2, and some ATP is produced. Once citrate has formed, the citrate then goes on to step 2 in which it is transformed into an isomer molecule called ...
Two step reaction diagram. Arrhenius Theory and Reaction Coordinates - Chemistry 302 The reaction above has three steps (three barriers) and two intermediates. On the far left of the diagram are the reactant species and on the far right are the product species. ... instead point B is all the intermediate chemical species that exist after the first step. Reaction mechanisms also have "fast" and "slow" steps. We can always ... 2 step reaction coordinate diagram - YouTube goes through the SN1 reaction between 2-bromo-2-methylpropane and chloride ion to form 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and bromide ion. Details of reaction coordina... Energy Diagrams of Two Step Reactions - YouTube Watch Complete videos @ Organic Chemistry 1 Multistep Reactions - Softschools.com The energy diagram of a two-step reaction is shown below. In the above reaction, a reactant goes through one elementary step with a lower activation energy (transition state 1) to form the intermediate. The intermediate then goes through a second step (transition state 2) with the highest energy barrier to form the product.
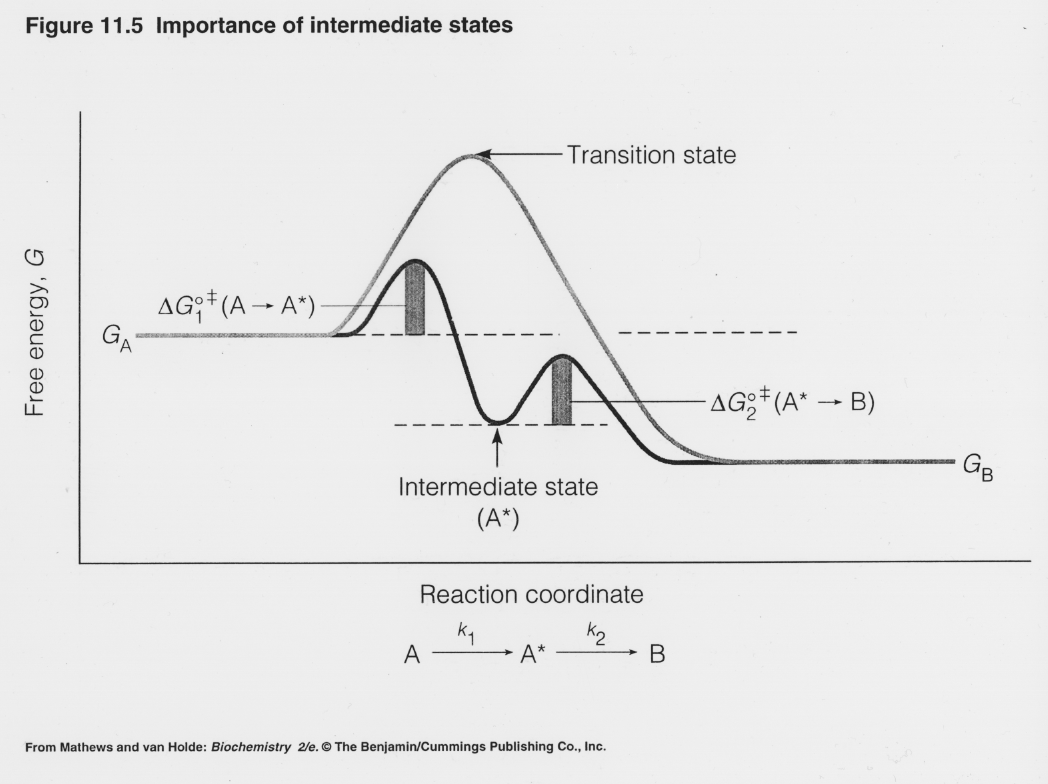
Reaction Mechanisms - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian Edition A potential energy diagram for this multi-step reaction can be drawn as shown in Figure 17.12 "Multi-step Reaction Potential Energy Diagram." Notice each step has its own activation energy, and transition state (or activated complex), which is the highest-energy transitional point in the elementary step. Transition states are very unstable ... PDF Potential energy diagram for a two-step sequential reaction Reaction coordinate step 1 step 2 A B C A B C k 1 k 2 B (point 3) is an intermediate . Title: Energy_Diagram_Two_Steps.xls Author: james Created Date: Solved Choose the energy diagram for a two-step reaction, A - Chegg Choose the energy diagram for a two-step reaction, A → B → C, in which the relative energy of the compounds is A< C < B, and the step A→ B is rate-determining. Select the single best answer. Reaction coordinate Reaction coordinate IV. Reaction coordinate Reaction coordinate II O IV References eBook & Resources Multipart Answer Difficulty: Medium Energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction that is exothermic overall, and consists of a fast but endothermic first step, and a slow but exothermic second step. Indicate DGrxn, as well as DG1* and DG2* for the first and second activation energies, respectively. Label the positions corresponding to the transition states with an asterisk.
[Solved] Please see an attachment for details | Course Hero Draw a potential energy diagram for a two-step reaction in which the activation energies are 10 kcal/mol (first step) and 3 kcal/mole (second step), the intermediate is 5 kcal/mol higher in energy than the reactants, and the products are 1 kcal/mol lower in energy than the reactants. Label both axes and positions on the curve that correspond to ... SOLVED:Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in ... Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in which the first step is endergonic, the second step is exergonic, and the overall reaction is endergonic. Label the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states. Answer View Answer Discussion You must be signed in to discuss. Watch More Solved Questions in Chapter 3 Identifying Steps in a Reaction Profile Diagram for a Two-Step Chemical ... The reaction-profile diagram for a two-step chemical reaction is shown below. In step 1, compound a reacts to form compound b, and in step two, compound b reacts to form compound c. Which step has the highest activation energy? Which step is an exothermic reaction? The portal has been deactivated. Please contact your portal admin. 6. Reaction Coordinate Diagram - VIZISCIENCE® INTERACTIVE LABS The reaction involves two steps, step 1 is the slowest step and step 2 is the fastest step. Both steps are exothermic. Indicate on the diagram the overall enthalpy change of the reaction, the reaction for the transition states and intermediate states. The reaction is a reaction between hydrogen gas and brown vapor of iodine monochloride.
SOLVED:Draw an energy diagram for a two-step exergonic reaction whose ... in this question. We're going to draw the energy during um for two step reaction where the second step of the reaction is faster than the first step of the reaction. It's no. Let's recall the definition of Gibbs free energy change and that is the difference between the free energy of the products. My enough see free energy of the reactant. It's so yeah, the gifts rich free energy change is ...
Multistep reaction energy profiles (video) - Khan Academy Many chemical reactions have mechanisms that consist of multiple elementary steps. The energy profile for a multistep reaction can be used to compare the activation energies of the different steps and identify the rate-determining step. The energy profile can also be used to determine the overall change in energy for the reaction. Created by Jay.
7.2 SN2 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry Energy Diagram of SN2 Mechanism. The energy changes for the above reaction can be represented in the energy diagram shown in Fig. 7.1. S N 2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram has only one curve. The products CH 3 OH and Br - are in lower energy than the reactants CH 3 Br and OH -, indicates that the overall reaction is exothermic ...
Solved Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. - Chegg Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. enthalpy change transition state starting materials RX+H products rate-limiting transition state intermediates activation energy reaction coordinate.
How do you find the rate determining step from a graph? The rate determining step in a reaction mechanism is the slowest step. It is characterized by its high activation energy. Consider the energy diagram represented below of a two-step mechanism. The first step is the slow step since it has the highest activation energy. Here is more about this topic in the following video:
Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism Jun 01, 2022 · Complete Energy Diagram for Two-Step Reaction A Two-Step Reaction Mechanism The transition states are located at energy maxima. The reactive intermediate B+ is located at an energy minimum. Each step has its own delta H and activation energy. The overall energy difference between the starting materials and products is delta H overall.
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction i - Quizlet Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step reaction in which the first step is endergonic, the second step is exergonic, and the overall reaction is endergonic. Label the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states. Explanation Verified Reveal next step Reveal all steps Create a free account to see explanations
Two Step Exothermic Reaction 001 - YouTube Draw a reaction coordinate for the following catalyzed two-step exothermic reaction with the first step being the rate determining step:A -- B
7 Krebs Cycle Steps and Process: Diagram, Explanation Therefore, it is a two-step reaction sequence. The Krebs cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration. During the Krebs cycle, energy stored in pyruvate is transferred to NADH and FADH 2, and some ATP is produced. Once citrate has formed, the citrate then goes on to step 2 in which it is transformed into an isomer molecule called ...

Post a Comment for "44 two step reaction diagram"